PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 005
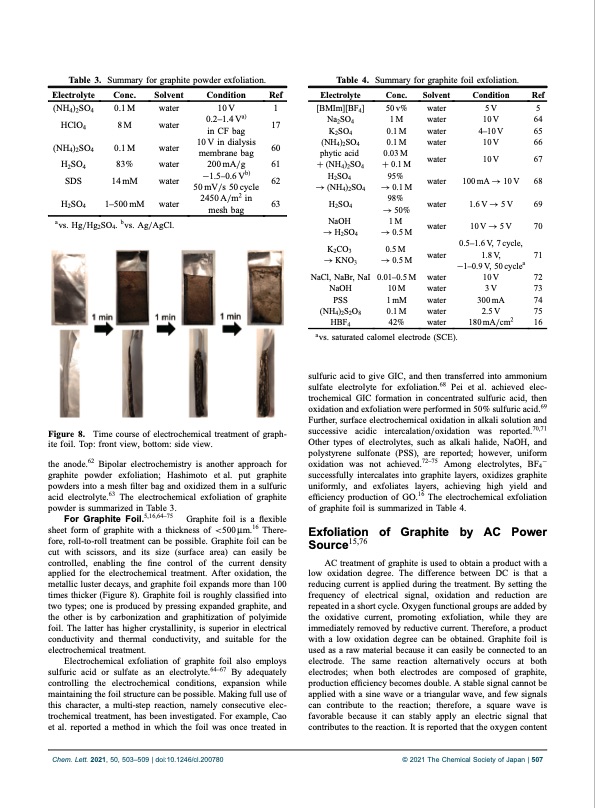
Table 3. Summary for graphite powder exfoliation. Table 4. Summary for graphite foil exfoliation. Electrolyte (NH4)2SO4 HClO4 (NH4)2SO4 H2SO4 SDS H SO 24 Conc. 0.1 M 8 M 0.1 M 83% 14 mM 1500mM Solvent water water water water water water Condition 10 V 0.21.4 Va) in CF bag 10 V in dialysis membrane bag 200 mA/g 11.50.6 Vb) 50 mV/s 50 cycle 2450A/m2 in mesh bag Ref 1 17 60 61 62 63 Electrolyte [BMIm][BF4] Na2SO4 K2SO4 (NH4)2SO4 phytic acid + (NH4)2SO4 H2SO4 1⁄4 (NH4)2SO4 H SO 2 4 NaOH 1⁄4 H2SO4 K2CO3 Conc. 50 v% 1 M 0.1 M 0.1 M 0.03 M + 0.1 M 95% 1⁄4 0.1 M 98% 1⁄4 50% 1M 1⁄4 0.5 M 0.5 M Solvent water water water water water water water water water water water water water water Condition Ref 5V5 10V 64 410 V 65 10V 66 10V 67 100mA 1⁄4 10V 68 1.6V 1⁄4 5V 69 10V1⁄45V 70 0.51.6 V, 7 cycle, 1.8V, 71 110.9V, 50cyclea 10V 72 3V 73 300mA 74 2.5 V 75 180 mA/cm2 16 avs. Hg/Hg2SO4. bvs. Ag/AgCl. Time course of electrochemical treatment of graph- sulfuric acid to give GIC, and then transferred into ammonium sulfate electrolyte for exfoliation.68 Pei et al. achieved elec- trochemical GIC formation in concentrated sulfuric acid, then oxidation and exfoliation were performed in 50% sulfuric acid.69 Further, surface electrochemical oxidation in alkali solution and successive acidic intercalation/oxidation was reported.70,71 Other types of electrolytes, such as alkali halide, NaOH, and polystyrene sulfonate (PSS), are reported; however, uniform oxidation was not achieved.7275 Among electrolytes, BF41 successfully intercalates into graphite layers, oxidizes graphite uniformly, and exfoliates layers, achieving high yield and efficiency production of GO.16 The electrochemical exfoliation of graphite foil is summarized in Table 4. Exfoliation of Graphite by AC Power Source15,76 AC treatment of graphite is used to obtain a product with a low oxidation degree. The difference between DC is that a reducing current is applied during the treatment. By setting the frequency of electrical signal, oxidation and reduction are repeated in a short cycle. Oxygen functional groups are added by the oxidative current, promoting exfoliation, while they are immediately removed by reductive current. Therefore, a product with a low oxidation degree can be obtained. Graphite foil is used as a raw material because it can easily be connected to an electrode. The same reaction alternatively occurs at both electrodes; when both electrodes are composed of graphite, production efficiency becomes double. A stable signal cannot be applied with a sine wave or a triangular wave, and few signals can contribute to the reaction; therefore, a square wave is favorable because it can stably apply an electric signal that contributes to the reaction. It is reported that the oxygen content Figure 8. ite foil. Top: front view, bottom: side view. the anode.62 Bipolar electrochemistry is another approach for graphite powder exfoliation; Hashimoto et al. put graphite powders into a mesh filter bag and oxidized them in a sulfuric acid electrolyte.63 The electrochemical exfoliation of graphite powder is summarized in Table 3. For Graphite Foil.5,16,6475 Graphite foil is a flexible sheet form of graphite with a thickness of <500 ̄m.16 There- fore, roll-to-roll treatment can be possible. Graphite foil can be cut with scissors, and its size (surface area) can easily be controlled, enabling the fine control of the current density applied for the electrochemical treatment. After oxidation, the metallic luster decays, and graphite foil expands more than 100 times thicker (Figure 8). Graphite foil is roughly classified into two types; one is produced by pressing expanded graphite, and the other is by carbonization and graphitization of polyimide foil. The latter has higher crystallinity, is superior in electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, and suitable for the electrochemical treatment. Electrochemical exfoliation of graphite foil also employs sulfuric acid or sulfate as an electrolyte.6467 By adequately controlling the electrochemical conditions, expansion while maintaining the foil structure can be possible. Making full use of this character, a multi-step reaction, namely consecutive elec- trochemical treatment, has been investigated. For example, Cao et al. reported a method in which the foil was once treated in 1⁄4KNO 1⁄40.5M 3 NaCl, NaBr, NaI 0.010.5 M NaOH 10M PSS 1mM (NH4)2S2O8 0.1 M HBF4 42% avs. saturated calomel electrode (SCE). Chem. Lett. 2021, 50, 503–509 | doi:10.1246/cl.200780 © 2021 The Chemical Society of Japan | 507PDF Image | Electrochemical Production of Graphene Analogs
PDF Search Title:
Electrochemical Production of Graphene AnalogsOriginal File Name Searched:
cl-200780.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Salgenx Redox Flow Battery Technology: Power up your energy storage game with Salgenx Salt Water Battery. With its advanced technology, the flow battery provides reliable, scalable, and sustainable energy storage for utility-scale projects. Upgrade to a Salgenx flow battery today and take control of your energy future.
CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com (Standard Web Page)