
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 024
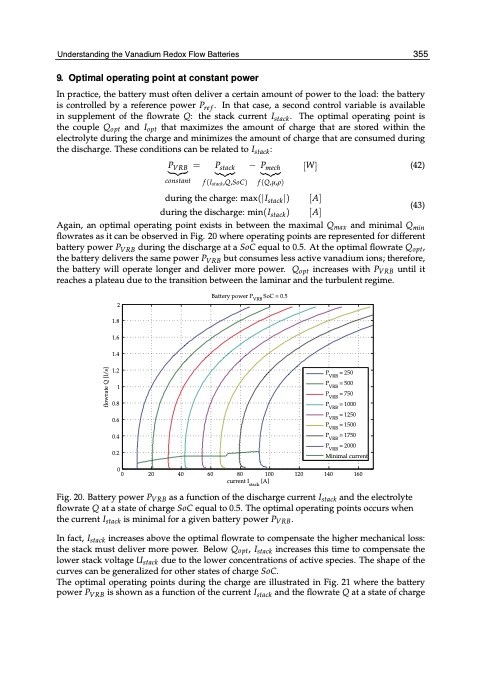
UnderstandininggththeeVVaannaaddiuimumRRedeodxoFxloFwlowBaBttaetrtiesries 32535 9. Optimal operating point at constant power In practice, the battery must often deliver a certain amount of power to the load: the battery is controlled by a reference power Pre f . In that case, a second control variable is available in supplement of the flowrate Q: the stack current Istack. The optimal operating point is the couple Qopt and Iopt that maximizes the amount of charge that are stored within the electrolyte during the charge and minimizes the amount of charge that are consumed during the discharge. These conditions can be related to Istack: PVRB = Pstack − Pmech [W] (42) constant f(Istack,Q,SoC) f(Q,μ,ρ) during the charge: max(|Istack|) [A] during the discharge: min(Istack) [A] (43) Again, an optimal operating point exists in between the maximal Qmax and minimal Qmin flowrates as it can be observed in Fig. 20 where operating points are represented for different battery power PVRB during the discharge at a SoC equal to 0.5. At the optimal flowrate Qopt, the battery delivers the same power PVRB but consumes less active vanadium ions; therefore, the battery will operate longer and deliver more power. Qopt increases with PVRB until it reaches a plateau due to the transition between the laminar and the turbulent regime. Battery power PVRB SoC = 0.5 2 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Fig. 20. Battery power PVRB as a function of the discharge current Istack and the electrolyte flowrate Q at a state of charge SoC equal to 0.5. The optimal operating points occurs when the current Istack is minimal for a given battery power PVRB. In fact, Istack increases above the optimal flowrate to compensate the higher mechanical loss: the stack must deliver more power. Below Qopt, Istack increases this time to compensate the lower stack voltage Ustack due to the lower concentrations of active species. The shape of the curves can be generalized for other states of charge SoC. The optimal operating points during the charge are illustrated in Fig. 21 where the battery power PVRB is shown as a function of the current Istack and the flowrate Q at a state of charge PVRB = 250 PVRB = 500 PVRB = 750 PVRB = 1000 PVRB = 1250 PVRB = 1500 PVRB = 1750 PVRB = 2000 Minimal current 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 current Istack [A] flowrate Q [l/s]PDF Image | Understanding the Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries
PDF Search Title:
Understanding the Vanadium Redox Flow BatteriesOriginal File Name Searched:
12523.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Salgenx Redox Flow Battery Technology: Salt water flow battery technology with low cost and great energy density that can be used for power storage and thermal storage. Let us de-risk your production using our license. Our aqueous flow battery is less cost than Tesla Megapack and available faster. Redox flow battery. No membrane needed like with Vanadium, or Bromine. Salgenx flow battery
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@salgenx.com | RSS | AMP |