
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 008
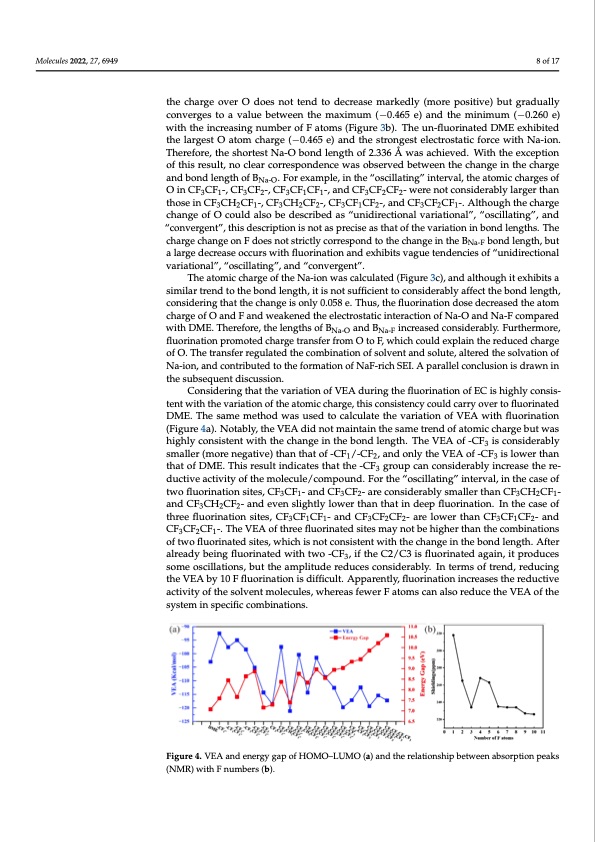
Molecules 2022, 27, 6949 8 of 17 the charge over O does not tend to decrease markedly (more positive) but gradually converges to a value between the maximum (−0.465 e) and the minimum (−0.260 e) Molecules 2022, 27, x FOR PEER REVIEW 8 of 17 with the increasing number of F atoms (Figure 3b). The un-fluorinated DME exhibited the largest O atom charge (−0.465 e) and the strongest electrostatic force with Na-ion. Therefore, the shortest Na-O bond length of 2.336 Å was achieved. With the exception of this result, no clear correspondence was observed between the change in the charge lengthof2.336Å wasachieved.Withtheexceptionofthisresult,noclearcorrespondencewas and bond length of B . For example, in the “oscillating” interval, the atomic charges of observed between the cNhaa-Onge in the charge and bond length of BNa-O. For example, in the “os- OinCF CF -,CF CF -,CF CF CF -,andCF CF CF -werenotconsiderablylargerthan cillating”3inte1rval, t3he a2tomic3cha1rges1 of O in CF3 3CF21-, C2F3CF2-, CF3CF1CF1-, and CF3CF2CF2- thoseinCF CH CF -,CF CH CF -,CF CF CF -,andCF CF CF -.Althoughthecharge were not co3nsid2erab1ly lar3ger 2than2 thos3e in1 CF23CH2CF1-,3CF32CH12CF2-, CF3CF1CF2-, and change of O could also be described as “unidirectional variational”, “oscillating”, and CF3CF2CF1-. Although the charge change of O could also be described as “unidirectional var- “convergent”, this description is not as precise as that of the variation in bond lengths. The iational”, “oscillating”, and “convergent”, this description is not as precise as that of the vari- charge change on F does not strictly correspond to the change in the B bond length, but ation in bond lengths. The charge change on F does not strictly correspoNnad-Fto the change in a large decrease occurs with fluorination and exhibits vague tendencies of “unidirectional the BNa-F bond length, but a large decrease occurs with fluorination and exhibits vague variational”, “oscillating”, and “convergent”. tendencies of “unidirectional variational”, “oscillating”, and “convergent”. The atomic charge of the Na-ion was calculated (Figure 3c), and although it exhibits a The atomic charge of the Na-ion was calculated (Figure 3c), and although it exhibits similar trend to the bond length, it is not sufficient to considerably affect the bond length, a similar trend to the bond length, it is not sufficient to considerably affect the bond length, considering that the change is only 0.058 e. Thus, the fluorination dose decreased the atom considering that the change is only 0.058 e. Thus, the fluorination dose decreased the atom charge of O and F and weakened the electrostatic interaction of Na-O and Na-F compared charge of O and F and weakened the electrostatic interaction of Na-O and Na-F compared with DME. Therefore, the lengths of BNa-O and BNa-F increased considerably. Furthermore, with DME. Therefore, the lengths of BNa-O and BNa-F increased considerably. Furthermore, fluorination promoted charge transfer from O to F, which could explain the reduced charge fluorination promoted charge transfer from O to F, which could explain the reduced charge of O. The transfer regulated the combination of solvent and solute, altered the solvation of of O. The transfer regulated the combination of solvent and solute, altered the solvation of Na-ion, and contributed to the formation of NaF-rich SEI. A parallel conclusion is drawn in Na-ion, and contributed to the formation of NaF-rich SEI. A parallel conclusion is drawn in the subsequent discussion. the subsequent discussion. Considering that the variation of VEA during the fluorination of EC is highly consis- Considering that the variation of VEA during the fluorination of EC is highly con- tent with the variation of the atomic charge, this consistency could carry over to fluorinated sistent with the variation of the atomic charge, this consistency could carry over to fluori- DME. The same method was used to calculate the variation of VEA with fluorination nated DME. The same method was used to calculate the variation of VEA with fluorination (Figure 4a). Notably, the VEA did not maintain the same trend of atomic charge but was (Figure 4a). Notably, the VEA did not maintain the same trend of atomic charge but was highly highly consistent with the change in the bond length. The VEA of -CF3 is considerably consistent with the change in the bond length. The VEA of -CF3 is considerably smaller (more smaller (more negative) than that of -CF1/-CF2, and only the VEA of -CF3 is lower than negative) than that of -CF1/-CF2, and only the VEA of -CF3 is lower than that of DME. This that of DME. This result indicates that the -CF3 group can considerably increase the re- result indicates that the -CF3 group can considerably increase the reductive activity of the mol- ductive activity of the molecule/compound. For the “oscillating” interval, in the case of ecule/compound. For the “oscillating” interval, in the case of two fluorination sites, CF3CF1- two fluorination sites, CF3CF1- and CF3CF2- are considerably smaller than CF3CH2CF1- and CF3CF2- are considerably smaller than CF3CH2CF1- and CF3CH2CF2- and even slightly and CF3CH2CF2- and even slightly lower than that in deep fluorination. In the case of lower than that in deep fluorination. In the case of three fluorination sites, CF3CF1CF1- and three fluorination sites, CF3CF1CF1- and CF3CF2CF2- are lower than CF3CF1CF2- and CF3CF2CF2- are lower than CF3CF1CF2- and CF3CF2CF1-. The VEA of three fluorinated sites CF3CF2CF1-. The VEA of three fluorinated sites may not be higher than the combinations may not be higher than the combinations of two fluorinated sites, which is not consistent of two fluorinated sites, which is not consistent with the change in the bond length. After with the change in the bond length. After already being fluorinated with two -CF3, if the already being fluorinated with two -CF3, if the C2/C3 is fluorinated again, it produces C2/C3 is fluorinated again, it produces some oscillations, but the amplitude reduces con- some oscillations, but the amplitude reduces considerably. In terms of trend, reducing siderably. In terms of trend, reducing the VEA by 10 F fluorination is difficult. Apparently, the VEA by 10 F fluorination is difficult. Apparently, fluorination increases the reductive fluorination increases the reductive activity of the solvent molecules, whereas fewer F at- activity of the solvent molecules, whereas fewer F atoms can also reduce the VEA of the oms can also reduce the VEA of the system in specific combinations. system in specific combinations. FFigiguurree44..VVEEAAaannddeenneergrgyyggaappooffHHOOMOO––LLUUMOO(a(a))aannddththeererelalatitoionnsshhipipbbeetwtweeennaabbssoorrpptitoionnppeeaakkss (NMR) with F numbers (b). (NMR) with F numbers (b). We speculated that fluorinated DME should exhibit a wider ESW and calculated the HOMO–LUMO energy gap of fluorinated DME with the Na-ion system under the same en- vironment (Figure 4a). The results revealed that the energy gap is already larger than the fluorinated EC when the fluorination degree reached 3 F or more. The change in the energy gap differs from the existing pattern, and “unidirectional variational”, “oscillating”, andPDF Image | First-Principles-Based Optimized Design of Fluoride Electrolytes
PDF Search Title:
First-Principles-Based Optimized Design of Fluoride ElectrolytesOriginal File Name Searched:
molecules-27-06949.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Salgenx Redox Flow Battery Technology: Salt water flow battery technology with low cost and great energy density that can be used for power storage and thermal storage. Let us de-risk your production using our license. Our aqueous flow battery is less cost than Tesla Megapack and available faster. Redox flow battery. No membrane needed like with Vanadium, or Bromine. Salgenx flow battery
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@salgenx.com | RSS | AMP |