
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 006
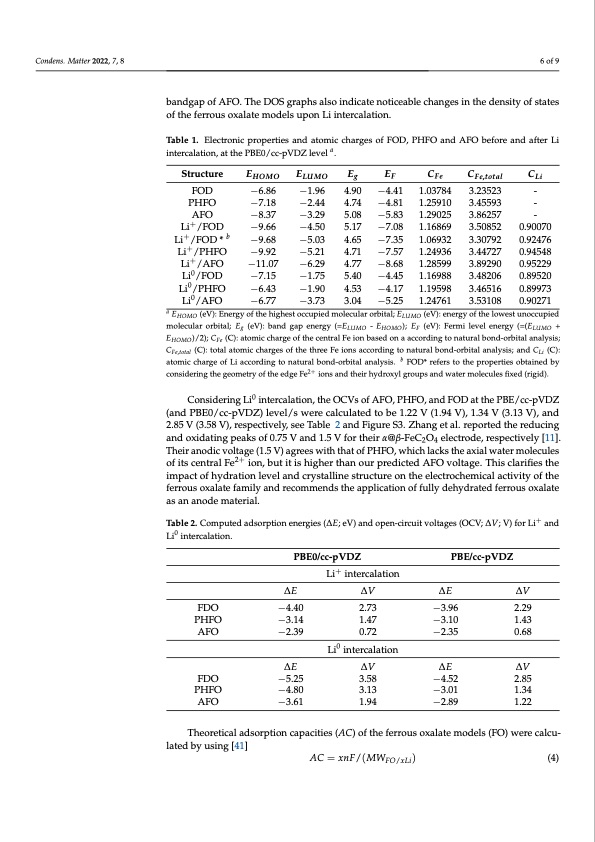
Condens. Matter 2022, 7, 8 6 of 9 bandgap of AFO. The DOS graphs also indicate noticeable changes in the density of states of the ferrous oxalate models upon Li intercalation. Table 1. Electronic properties and atomic charges of FOD, PHFO and AFO before and after Li intercalation, at the PBE0/cc-pVDZ level a. Structure FOD PHFO AFO Li+ /FOD Li+/FOD * b Li+ /PHFO Li+ /AFO EHOMO −6.86 −7.18 −8.37 −9.66 −9.68 −9.92 −11.07 ELUMO Eg −1.96 4.90 −2.44 4.74 −3.29 5.08 −4.50 5.17 −5.03 4.65 −5.21 4.71 −6.29 4.77 −1.75 5.40 −1.90 4.53 −3.73 3.04 EF CFe −4.41 1.03784 −4.81 1.25910 −5.83 1.29025 −7.08 1.16869 −7.35 1.06932 −7.57 1.24936 −8.68 1.28599 −4.45 1.16988 −4.17 1.19598 −5.25 1.24761 CFe,total 3.23523 3.45593 3.86257 3.50852 3.30792 3.44727 3.89290 3.48206 3.46516 3.53108 CLi - - - 0.90070 0.92476 0.94548 0.95229 0.89520 0.89973 0.90271 Li0/FOD −7.15 Li0/PHFO −6.43 Li0/AFO −6.77 a EHOMO (eV): Energy of the highest occupied molecular orbital; ELUMO (eV): energy of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital; Eg (eV): band gap energy (=ELUMO - EHOMO); EF (eV): Fermi level energy (=(ELUMO + EHOMO)/2); CFe (C): atomic charge of the central Fe ion based on a according to natural bond-orbital analysis; CFe,total (C): total atomic charges of the three Fe ions according to natural bond-orbital analysis; and CLi (C): atomic charge of Li according to natural bond-orbital analysis. b FOD* refers to the properties obtained by considering the geometry of the edge Fe2+ ions and their hydroxyl groups and water molecules fixed (rigid). Considering Li0 intercalation, the OCVs of AFO, PHFO, and FOD at the PBE/cc-pVDZ (and PBE0/cc-pVDZ) level/s were calculated to be 1.22 V (1.94 V), 1.34 V (3.13 V), and 2.85 V (3.58 V), respectively, see Table 2 and Figure S3. Zhang et al. reported the reducing and oxidating peaks of 0.75 V and 1.5 V for their α@β-FeC2O4 electrode, respectively [11]. Their anodic voltage (1.5 V) agrees with that of PHFO, which lacks the axial water molecules of its central Fe2+ ion, but it is higher than our predicted AFO voltage. This clarifies the impact of hydration level and crystalline structure on the electrochemical activity of the ferrous oxalate family and recommends the application of fully dehydrated ferrous oxalate as an anode material. Table 2. Computed adsorption energies (∆E; eV) and open-circuit voltages (OCV; ∆V; V) for Li+ and Li0 intercalation. PBE0/cc-pVDZ PBE/cc-pVDZ Li+ intercalation ∆E ∆V ∆E ∆V FDO −4.40 2.73 PHFO −3.14 1.47 AFO −2.39 0.72 Li0 intercalation −3.96 2.29 −3.10 1.43 −2.35 0.68 ∆E ∆V ∆E ∆V FDO −5.25 3.58 PHFO −4.80 3.13 AFO −3.61 1.94 −4.52 2.85 −3.01 1.34 −2.89 1.22 Theoretical adsorption capacities (AC) of the ferrous oxalate models (FO) were calcu- lated by using [41] AC = xnF/(MWFO/xLi) (4)PDF Image | Anodic Activity of Hydrated and Anhydrous Iron (II) Oxalate in Li-Ion Batteries
PDF Search Title:
Anodic Activity of Hydrated and Anhydrous Iron (II) Oxalate in Li-Ion BatteriesOriginal File Name Searched:
condensedmatter-07-00008.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2 Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2. Gamma sulfur also known as mother of pearl sulfur and nacreous sulfur... More Info
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |