
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 026
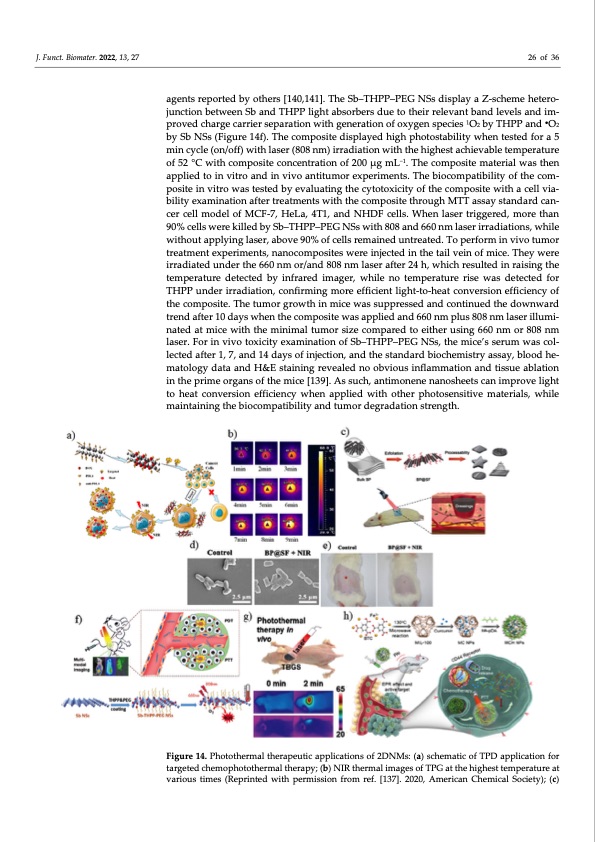
J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 27 26 of 36 agents reported by others [140,141]. The Sb–THPP–PEG NSs display a Z-scheme hetero- junction between Sb and THPP light absorbers due to their relevant band levels and im- proved charge carrier separation with generation of oxygen species 1O2 by THPP and ●O2 by Sb NSs (Figure 14f). The composite displayed high photostability when tested for a 5 min cycle (on/off) with laser (808 nm) irradiation with the highest achievable temperature of 52 °C with composite concentration of 200 μg mL−1. The composite material was then applied to in vitro and in vivo antitumor experiments. The biocompatibility of the com- posite in vitro was tested by evaluating the cytotoxicity of the composite with a cell via- bility examination after treatments with the composite through MTT assay standard can- cer cell model of MCF-7, HeLa, 4T1, and NHDF cells. When laser triggered, more than 90% cells were killed by Sb–THPP–PEG NSs with 808 and 660 nm laser irradiations, while without applying laser, above 90% of cells remained untreated. To perform in vivo tumor treatment experiments, nanocomposites were injected in the tail vein of mice. They were irradiated under the 660 nm or/and 808 nm laser after 24 h, which resulted in raising the temperature detected by infrared imager, while no temperature rise was detected for THPP under irradiation, confirming more efficient light-to-heat conversion efficiency of the composite. The tumor growth in mice was suppressed and continued the downward trend after 10 days when the composite was applied and 660 nm plus 808 nm laser illumi- nated at mice with the minimal tumor size compared to either using 660 nm or 808 nm laser. For in vivo toxicity examination of Sb–THPP–PEG NSs, the mice’s serum was col- lected after 1, 7, and 14 days of injection, and the standard biochemistry assay, blood he- matology data and H&E staining revealed no obvious inflammation and tissue ablation in the prime organs of the mice [139]. As such, antimonene nanosheets can improve light to heat conversion efficiency when applied with other photosensitive materials, while maintaining the biocompatibility and tumor degradation strength. Figure 14. Photothermal therapeutic applications of 2DNMs: (a) schematic of TPD application for targeted chemophotothermal therapy; (b) NIR thermal images of TPG at the highest temperature at various times (Reprinted with permission from ref. [137]. 2020, American Chemical Society); (c)PDF Image | Nanomaterials beyond Graphene for Biomedical Applications
PDF Search Title:
Nanomaterials beyond Graphene for Biomedical ApplicationsOriginal File Name Searched:
jfb-13-00027.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |