
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 008
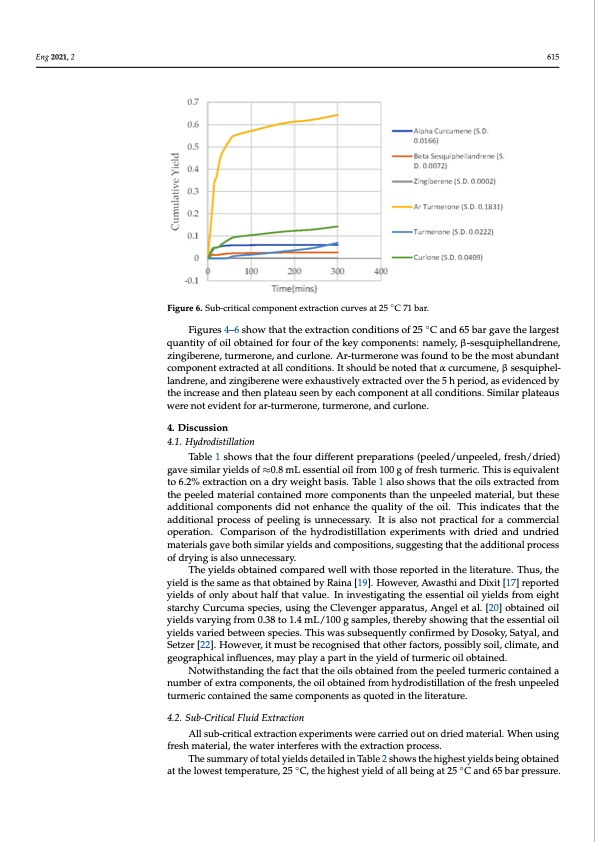
Eng 2021, 2 615 Figure 5. Sub-critical component extraction curves at 25 °C 68 bar. Figure 6. Sub-critical component extraction curves at 25 ◦C 71 bar. Figure 6. Sub-critical component extraction curves at 25 °C 71 bar. quantity of oil obtained for four of the key components: namely, β-sesquiphellandrene, zingiberene, turmerone, and curlone. Ar-turmerone waTs hfoeu%ndoftothbe KtheeymCosmt pabounnendtasnt component extracted at all conditions. It should be noted that α curcumene, β sesquiphel- Temperature in °C Pressure in Bar Determined in the landrene, and zingiberene were exhaustively extracted over the 5 h period, as evidenced by Figures 4–6 show that the extraction conditions of 25 ◦C and 65 bar gave the largest Table 3. The percentage of key components as a function of temperature and pressure. the increase and then plateau seen by each component at all conditions. Similar plateaus 4.1. Hydrodistillation 25 65 70.9 were not evident for ar-turmerone, turmerone, and curlone. 4. Discussion 25 68 50.9 25 71 53.2 27 65 54.2 27 68 47.2 Table 1 shows that the four different preparations (peeled/unpeeled, fresh/dried) 27 71 46.2 gave similar yields of ≈0.8 mL essential oil from 100 g of fresh turmeric. This is equivalent 30 65 39.6 to 6.2% extraction on a dry weight basis. Table 1 also shows that the oils extracted from 30 68 46.7 the peeled material contained more components than the unpeeled material, but these 30 71 44.9 additional components did not enhance the quality of the oil. This indicates that the additional process of peeling is unnecessary. It is also not practical for a commercial Figures 4–6 show that the extraction conditions of 25 °C and 65 bar gave the largest operation. Comparison of the hydrodistillation experiments with dried and undried quantity of oil obtained for four of the key components: namely, β-sesquiphellandrene, materials gave both similar yields and compositions, suggesting that the additional process zoifndgribyeinregnies,atlusromuenrnoence,sasnardy.curlone. Ar-turmerone was found to be the most abundant compTohnenytielxdtsraocbtetadinatedallccoomnpdaitrieodnsw. Ietllshwoiuthldthboesneortepdotrhtaetdαincuthrceulmiternaet,uβres.esTqhuisp,htehle- lyainedldreisneth,eansdamzeinagsibthearetnoebtwaienredebxhyaRuasitnivae[l1y9]e.xHtroawctedveor,vAerwtahseth5ihanpderDioixdi,ta[1s7e]vriedpeonrcted yields of only about half that value. In investigating the essential oil yields from eight starchy Curcuma species, using the Clevenger apparatus, Angel et al. [20] obtained oil yields varying from 0.38 to 1.4 mL/100 g samples, thereby showing that the essential oil yields varied between species. This was subsequently confirmed by Dosoky, Satyal, and Setzer [22]. However, it must be recognised that other factors, possibly soil, climate, and geographical influences, may play a part in the yield of turmeric oil obtained. Notwithstanding the fact that the oils obtained from the peeled turmeric contained a number of extra components, the oil obtained from hydrodistillation of the fresh unpeeled turmeric contained the same components as quoted in the literature. 4.2. Sub-Critical Fluid Extraction All sub-critical extraction experiments were carried out on dried material. When using fresh material, the water interferes with the extraction process. The summary of total yields detailed in Table 2 shows the highest yields being obtained at the lowest temperature, 25 ◦C, the highest yield of all being at 25 ◦C and 65 bar pressure. ExtractPDF Image | Sub-Critical Fluid Extraction Turmeric vs Hydrodistillation
PDF Search Title:
Sub-Critical Fluid Extraction Turmeric vs HydrodistillationOriginal File Name Searched:
eng-02-00038.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |