
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 004
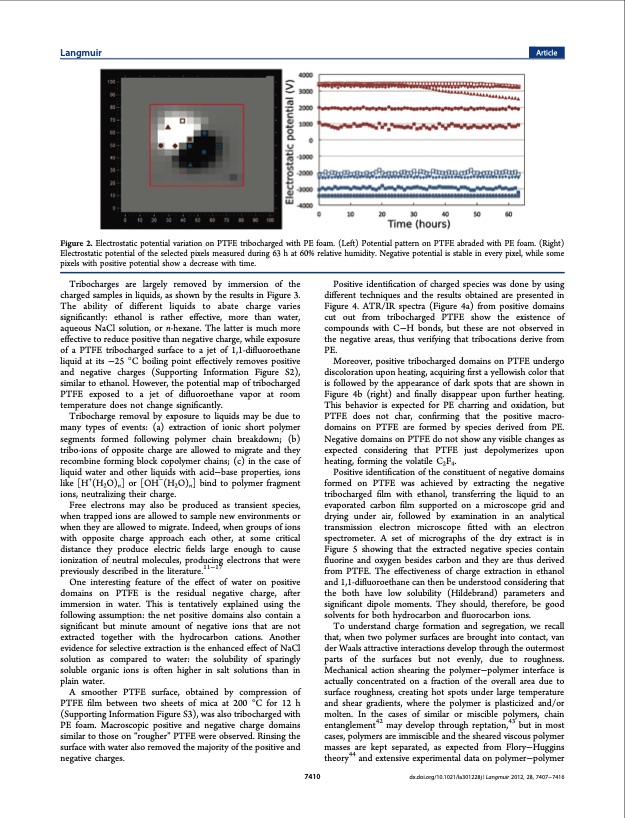
Langmuir Article Figure 2. Electrostatic potential variation on PTFE tribocharged with PE foam. (Left) Potential pattern on PTFE abraded with PE foam. (Right) Electrostatic potential of the selected pixels measured during 63 h at 60% relative humidity. Negative potential is stable in every pixel, while some pixels with positive potential show a decrease with time. Tribocharges are largely removed by immersion of the charged samples in liquids, as shown by the results in Figure 3. The ability of different liquids to abate charge varies significantly: ethanol is rather effective, more than water, aqueous NaCl solution, or n-hexane. The latter is much more effective to reduce positive than negative charge, while exposure of a PTFE tribocharged surface to a jet of 1,1-difluoroethane liquid at its −25 °C boiling point effectively removes positive and negative charges (Supporting Information Figure S2), similar to ethanol. However, the potential map of tribocharged PTFE exposed to a jet of difluoroethane vapor at room temperature does not change significantly. Tribocharge removal by exposure to liquids may be due to many types of events: (a) extraction of ionic short polymer segments formed following polymer chain breakdown; (b) tribo-ions of opposite charge are allowed to migrate and they recombine forming block copolymer chains; (c) in the case of liquid water and other liquids with acid−base properties, ions like [H+(H2O)n] or [OH−(H2O)n] bind to polymer fragment ions, neutralizing their charge. Free electrons may also be produced as transient species, when trapped ions are allowed to sample new environments or when they are allowed to migrate. Indeed, when groups of ions with opposite charge approach each other, at some critical distance they produce electric fields large enough to cause ionization of neutral molecules, producing electrons that were previously described in the literature.11−17 One interesting feature of the effect of water on positive domains on PTFE is the residual negative charge, after immersion in water. This is tentatively explained using the following assumption: the net positive domains also contain a significant but minute amount of negative ions that are not extracted together with the hydrocarbon cations. Another evidence for selective extraction is the enhanced effect of NaCl solution as compared to water: the solubility of sparingly soluble organic ions is often higher in salt solutions than in plain water. A smoother PTFE surface, obtained by compression of PTFE film between two sheets of mica at 200 °C for 12 h (Supporting Information Figure S3), was also tribocharged with PE foam. Macroscopic positive and negative charge domains similar to those on “rougher” PTFE were observed. Rinsing the surface with water also removed the majority of the positive and negative charges. Positive identification of charged species was done by using different techniques and the results obtained are presented in Figure 4. ATR/IR spectra (Figure 4a) from positive domains cut out from tribocharged PTFE show the existence of compounds with C−H bonds, but these are not observed in the negative areas, thus verifying that tribocations derive from PE. Moreover, positive tribocharged domains on PTFE undergo discoloration upon heating, acquiring first a yellowish color that is followed by the appearance of dark spots that are shown in Figure 4b (right) and finally disappear upon further heating. This behavior is expected for PE charring and oxidation, but PTFE does not char, confirming that the positive macro- domains on PTFE are formed by species derived from PE. Negative domains on PTFE do not show any visible changes as expected considering that PTFE just depolymerizes upon heating, forming the volatile C2F4. Positive identification of the constituent of negative domains formed on PTFE was achieved by extracting the negative tribocharged film with ethanol, transferring the liquid to an evaporated carbon film supported on a microscope grid and drying under air, followed by examination in an analytical transmission electron microscope fitted with an electron spectrometer. A set of micrographs of the dry extract is in Figure 5 showing that the extracted negative species contain fluorine and oxygen besides carbon and they are thus derived from PTFE. The effectiveness of charge extraction in ethanol and 1,1-difluoroethane can then be understood considering that the both have low solubility (Hildebrand) parameters and significant dipole moments. They should, therefore, be good solvents for both hydrocarbon and fluorocarbon ions. To understand charge formation and segregation, we recall that, when two polymer surfaces are brought into contact, van der Waals attractive interactions develop through the outermost parts of the surfaces but not evenly, due to roughness. Mechanical action shearing the polymer−polymer interface is actually concentrated on a fraction of the overall area due to surface roughness, creating hot spots under large temperature and shear gradients, where the polymer is plasticized and/or molten. In the cases of similar or miscible polymers, chain entanglement42 may develop through reptation,43 but in most cases, polymers are immiscible and the sheared viscous polymer masses are kept separated, as expected from Flory−Huggins theory44 and extensive experimental data on polymer−polymer 7410 dx.doi.org/10.1021/la301228j | Langmuir 2012, 28, 7407−7416PDF Image | Triboelectricity: Macroscopic Charge Patterns Formed by Self- Arraying Ions on Polymer Surfaces
PDF Search Title:
Triboelectricity: Macroscopic Charge Patterns Formed by Self- Arraying Ions on Polymer SurfacesOriginal File Name Searched:
la301228j.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
NFT (Non Fungible Token): Buy our tech, design, development or system NFT and become part of our tech NFT network... More Info
IT XR Project Redstone NFT Available for Sale: NFT for high tech turbine design with one part 3D printed counter-rotating energy turbine. Be part of the future with this NFT. Can be bought and sold but only one design NFT exists. Royalties go to the developer (Infinity) to keep enhancing design and applications... More Info
Infinity Turbine IT XR Project Redstone Design: NFT for sale... NFT for high tech turbine design with one part 3D printed counter-rotating energy turbine. Includes all rights to this turbine design, including license for Fluid Handling Block I and II for the turbine assembly and housing. The NFT includes the blueprints (cad/cam), revenue streams, and all future development of the IT XR Project Redstone... More Info
Infinity Turbine ROT Radial Outflow Turbine 24 Design and Worldwide Rights: NFT for sale... NFT for the ROT 24 energy turbine. Be part of the future with this NFT. This design can be bought and sold but only one design NFT exists. You may manufacture the unit, or get the revenues from its sale from Infinity Turbine. Royalties go to the developer (Infinity) to keep enhancing design and applications... More Info
Infinity Supercritical CO2 10 Liter Extractor Design and Worldwide Rights: The Infinity Supercritical 10L CO2 extractor is for botanical oil extraction, which is rich in terpenes and can produce shelf ready full spectrum oil. With over 5 years of development, this industry leader mature extractor machine has been sold since 2015 and is part of many profitable businesses. The process can also be used for electrowinning, e-waste recycling, and lithium battery recycling, gold mining electronic wastes, precious metals. CO2 can also be used in a reverse fuel cell with nafion to make a gas-to-liquids fuel, such as methanol, ethanol and butanol or ethylene. Supercritical CO2 has also been used for treating nafion to make it more effective catalyst. This NFT is for the purchase of worldwide rights which includes the design. More Info
NFT (Non Fungible Token): Buy our tech, design, development or system NFT and become part of our tech NFT network... More Info
Infinity Turbine Products: Special for this month, any plans are $10,000 for complete Cad/Cam blueprints. License is for one build. Try before you buy a production license. May pay by Bitcoin or other Crypto. Products Page... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |