
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 013
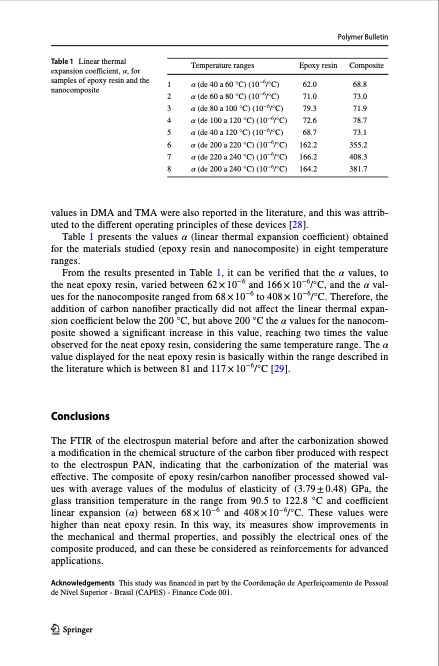
Polymer Bulletin Table 1 Linear thermal expansion coefficient, α, for samples of epoxy resin and the 1 nanocomposite 2 Temperature ranges α (de 40 a 60 °C) (10−6/°C) Epoxy resin Composite α (de 60 a 80 °C) (10−6/°C) 3 α (de 80 a 100 °C) (10−6/°C) 4 α (de 100 a 120 °C) (10−6/°C) 5 α (de 40 a 120 °C) (10−6/°C) 6 α (de 200 a 220 °C) (10−6/°C) 7 α (de 220 a 240 °C) (10−6/°C) 8 α (de 200 a 240 °C) (10−6/°C) 62.0 68.8 71.0 73.0 79.3 71.9 72.6 78.7 68.7 73.1 162.2 355.2 166.2 408.3 164.2 381.7 values in DMA and TMA were also reported in the literature, and this was attrib- uted to the different operating principles of these devices [28]. Table 1 presents the values α (linear thermal expansion coefficient) obtained for the materials studied (epoxy resin and nanocomposite) in eight temperature ranges. From the results presented in Table 1, it can be verified that the α values, to the neat epoxy resin, varied between 62 × 10−6 and 166 × 10−6/°C, and the α val- ues for the nanocomposite ranged from 68 × 10−6 to 408 × 10−6/°C. Therefore, the addition of carbon nanofiber practically did not affect the linear thermal expan- sion coefficient below the 200 °C, but above 200 °C the α values for the nanocom- posite showed a significant increase in this value, reaching two times the value observed for the neat epoxy resin, considering the same temperature range. The α value displayed for the neat epoxy resin is basically within the range described in the literature which is between 81 and 117 × 10−6/°C [29]. Conclusions The FTIR of the electrospun material before and after the carbonization showed a modification in the chemical structure of the carbon fiber produced with respect to the electrospun PAN, indicating that the carbonization of the material was effective. The composite of epoxy resin/carbon nanofiber processed showed val- ues with average values of the modulus of elasticity of (3.79±0.48) GPa, the glass transition temperature in the range from 90.5 to 122.8 °C and coefficient linear expansion (α) between 68 × 10−6 and 408 × 10−6/°C. These values were higher than neat epoxy resin. In this way, its measures show improvements in the mechanical and thermal properties, and possibly the electrical ones of the composite produced, and can these be considered as reinforcements for advanced applications. Acknowledgements This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001. 13PDF Image | Carbon nanofibers obtained from electrospinning process
PDF Search Title:
Carbon nanofibers obtained from electrospinning processOriginal File Name Searched:
Artigoelectrospinnigprocess2019.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2 Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2. Gamma sulfur also known as mother of pearl sulfur and nacreous sulfur... More Info
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |