
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 016
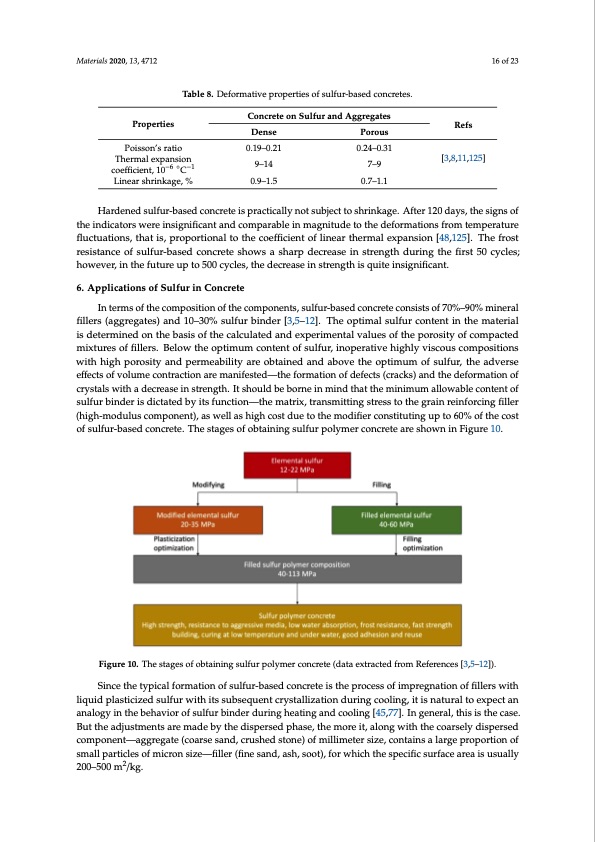
Materials 2020, 13, 4712 16 of 23 Properties Table 8. Deformative properties of sulfur-based concretes. Concrete on Sulfur and Aggregates Poisson’s ratio Thermal expansion coefficient, 10−6 ◦C−1 Linear shrinkage, % Dense 0.19–0.21 9–14 0.9–1.5 Porous 0.24–0.31 7–9 0.7–1.1 Refs [3,8,11,125] Hardened sulfur-based concrete is practically not subject to shrinkage. After 120 days, the signs of the indicators were insignificant and comparable in magnitude to the deformations from temperature fluctuations, that is, proportional to the coefficient of linear thermal expansion [48,125]. The frost resistance of sulfur-based concrete shows a sharp decrease in strength during the first 50 cycles; however, in the future up to 500 cycles, the decrease in strength is quite insignificant. 6. Applications of Sulfur in Concrete In terms of the composition of the components, sulfur-based concrete consists of 70%–90% mineral fillers (aggregates) and 10–30% sulfur binder [3,5–12]. The optimal sulfur content in the material is determined on the basis of the calculated and experimental values of the porosity of compacted mixtures of fillers. Below the optimum content of sulfur, inoperative highly viscous compositions with high porosity and permeability are obtained and above the optimum of sulfur, the adverse effects of volume contraction are manifested—the formation of defects (cracks) and the deformation of crystals with a decrease in strength. It should be borne in mind that the minimum allowable content of sulfur binder is dictated by its function—the matrix, transmitting stress to the grain reinforcing filler (high-modulus component), as well as high cost due to the modifier constituting up to 60% of the cost of sulfur-based concrete. The stages of obtaining sulfur polymer concrete are shown in Figure 10. Figure 10. The stages of obtaining sulfur polymer concrete (data extracted from References [3,5–12]). Since the typical formation of sulfur-based concrete is the process of impregnation of fillers with liquid plasticized sulfur with its subsequent crystallization during cooling, it is natural to expect an analogy in the behavior of sulfur binder during heating and cooling [45,77]. In general, this is the case. But the adjustments are made by the dispersed phase, the more it, along with the coarsely dispersed component—aggregate (coarse sand, crushed stone) of millimeter size, contains a large proportion of small particles of micron size—filler (fine sand, ash, soot), for which the specific surface area is usually 200–500 m2/kg.PDF Image | Critical Review on the Properties and Applications of Sulfur-Based Concrete
PDF Search Title:
Critical Review on the Properties and Applications of Sulfur-Based ConcreteOriginal File Name Searched:
materials-13-04712.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2 Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2. Gamma sulfur also known as mother of pearl sulfur and nacreous sulfur... More Info
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |