
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 006
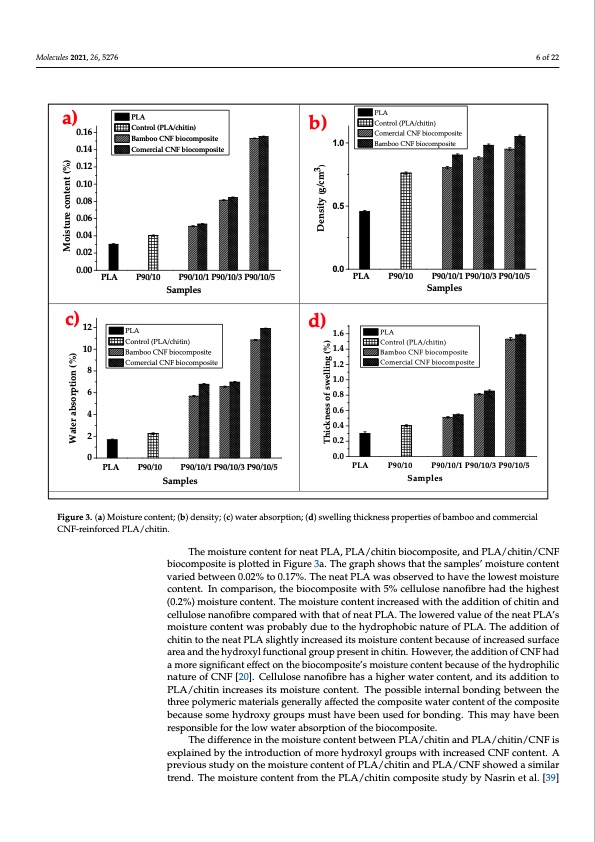
Molecules 2021, 26, 5276 6 of 22 Molecules 2021, 26, x FOR PEER REVIEW 6 of 23 a) 0.16 0.14 0.12 0.10 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0.00 PLA P90/10 P90/10/1 P90/10/3 P90/10/5 Samples b) 1.0 0.5 0.0 PLA P90/10 P90/10/1 P90/10/3 P90/10/5 Samples PLA Control (PLA/chitin) Comercial CNF biocomposite Bamboo CNF biocomposite PLA Control (PLA/chitin) Bamboo CNF biocomposite Comercial CNF biocomposite c)12 10 8 6 4 2 0 PLA Control (PLA/chitin) Bamboo CNF biocomposite Comercial CNF biocomposite PLA P90/10 P90/10/1 P90/10/3 P90/10/5 Samples d) 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 PLA Control (PLA/chitin) Bamboo CNF biocomposite Comercial CNF biocomposite PLA P90/10 Samples P90/10/1 P90/10/3 P90/10/5 Figure 3. (a) Moisture content; (b) density; (c) water absorption; (d) swelling thickness properties of bamboo and commer‐ Figure 3. (a) Moisture content; (b) density; (c) water absorption; (d) swelling thickness properties of bamboo and commercial cial CNF‐reinforced PLA/chitin. CNF-reinforced PLA/chitin. The moisture content for neat PLA, PLA/chitin biocomposite, and PLA/chitin/CNF The moisture content for neat PLA, PLA/chitin biocomposite, and PLA/chitin/CNF biocomposite is plotted in Figure 3a. The graph shows that the samples’ moisture content biocomposite is plotted in Figure 3a. The graph shows that the samples’ moisture content varied between 0.02% to 0.17%. The neat PLA was observed to have the lowest moisture varied between 0.02% to 0.17%. The neat PLA was observed to have the lowest moisture content. In comparison, the biocomposite with 5% cellulose nanofibre had the highest content. In comparison, the biocomposite with 5% cellulose nanofibre had the highest (0.2%) moisture content. The moisture content increased with the addition of chitin and (0.2%) moisture content. The moisture content increased with the addition of chitin and cellulose nanofibre compared with that of neat PLA. The lowered value of the neat PLA’s cellulose nanofibre compared with that of neat PLA. The lowered value of the neat PLA’s moisture content was probably due to the hydrophobic nature of PLA. The addition of moisture content was probably due to the hydrophobic nature of PLA. The addition of chitin to the neat PLA slightly increased its moisture content because of increased surface chitin to the neat PLA slightly increased its moisture content because of increased surface area and the hydroxyl functional group present in chitin. However, the addition of CNF area and the hydroxyl functional group present in chitin. However, the addition of CNF had had a more significant effect on the biocomposite’s moisture content because of the hy‐ a more significant effect on the biocomposite’s moisture content because of the hydrophilic drophilic nature of CNF [20]. Cellulose nanofibre has a higher water content, and its ad‐ nature of CNF [20]. Cellulose nanofibre has a higher water content, and its addition to dition to PLA/chitin increases its moisture content. The possible internal bonding between PLA/chitin increases its moisture content. The possible internal bonding between the theretehpreoelypmoleyrmicemriactemriatlesrgiaelnsegreanlleyralflfyecateffdecttheedctohmepcosmitpeowsiatteewr caotnertecnotnotfenthteocfothmepcoosmite‐ pboecsaituesbeescoamusehsyodmreoxhydgroxuypsgrmoupstshmavuestbheaevneubseednfuorsebdonfodrinbgo.ndTihnigs.mTahyishmavaye bheaevne bresepnornesipbolenfsoibrltehfeolrotwhewloawterwaabtseorrapbtisonrpotfiothneobfitohceombiopcoosmitep. osite. The difference in tthemooisisttuurreeccoonntetennt tbbetewtweenenPLPLAA/c/chhitiitninaannddPPLLAA//chiittiin/CNF is explained by the introduction of more hydroxyl groups with increased CNF content. A previous study on the moiistturecconttenttooffPPLLA//chitin and PLA/CNF showed a similar trend. The moisture content from the PLA/cchiittiin compossiittee ssttudy by Nasriin et al. [39] Water absorption (%) Moisture content (%) Thickness of swelling (%) Density (g/cm3)PDF Image | Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Isolation of Cellulose Nanofibre
PDF Search Title:
Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Isolation of Cellulose NanofibreOriginal File Name Searched:
molecules-26-05276-v2.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2 Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2. Gamma sulfur also known as mother of pearl sulfur and nacreous sulfur... More Info
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |