
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 009
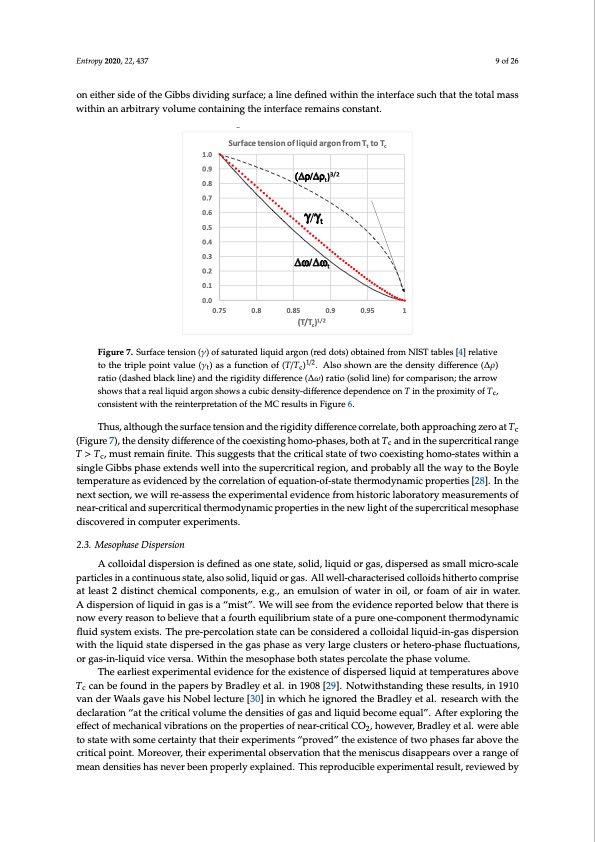
coexistingphaseswiththesameT,pandμ,i.e.,G =Aγ.Forallsubcriticalgas-liquidcoexistingstatesin s the 2-phase region both Gs and γ are positive, whence Gs and therefore Gtotal for the whole system is minimized by phase separation. For the equilibrium liquid in coexistence however, from the triple point to the critical point, the surface tension goes to zero. The difference between the rigidities of coexisting liquid and gaseous states (Δω = ωliq − ωgas) correlates with the surface tension (Figure 6). This Entropy 2020, 22, 437 9 of 26 can be explained: the difference in work required to increase the density of the coexisting states by adding molecules at constant volume is physically equivalent to the work required to create the inotnerefiathcerbsyidredoufctihnegGthibebdsednisviitdyinogf tshuerfliaqcue;ida alinde dsiemfiunletdanweiotuhisnlythinecirnetaesrifnagcethsuecdhetnhsaitythoef tohteavl ampaosusr ownietihtihneransiadreboitfrathrye Gvoiblubms deicvoidntinaignsinugrftahce;inatleirnfeacdeerfienmedainwsitchoinsthaneti.nterface such that the total mass within an arbitrary volume containing the interface remains constant. SurfacetensionofliquidargonfromTt toTc 1.0 (Δρ/Δρt)3/2 γ/γt Δω/Δωt 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0 0.75 0.8 0.85 0.9 (T/Tc)1/2 0.95 1 FFigiguurere77..SuSurfrafacecetetennssioionn(γ(γ))ooffsasatuturarateteddlilqiquiidarrgon(reddots)obtainedfromNIISTttaabbleless[4[4]]rerelalatitvivee 1/2 totoththeetrtirpipleleppoionitntvavlauleue(γ(t)γta)saas faunfucnticotnioonf o(Tf /(Tc/)Tc.) Al.soAslhsowshnoawrne tahre dtheensditeynsdiitfyfedreiffnecree(nΔcρe)(r∆aρti)o (dratsihoe(dabslahcekdlbinlaec)kanlidnet)haenrdigtihdeitryigdiidffietyrednicffee(rΔenωc)era(∆tiωo)(sroatlido (lsinoeli)dfolirnceo)mfopracroismopna; rtihseona;rrtohwe asrhrows thsahtowasrethaaltlaiqrueiadllaiqrugoidnasrghonwshaowcusbaicudbeicndsietnys-ditiyf-fderiffenercendcepdenpdenendceencoenonTTininttheproximityooffTTc,c, coconnsisitsetnenttwwitihthththeerereininteterprpreretatatitoionnooffththeeMCCreressuultlstsininFFigiguurree66.. Thus, although the surface tension and the rigidity difference correlate, both approaching zero at T Thus, although the surface tension and the rigidity difference correlate, both approaching zero at 1/2 (Figure7),thedensitydifferenceofthecoexistinghomo-phases,bothatT andinthesupercriticalrange c Tc (Figure 7), the density difference of the coexisting homo-phases, both at Tc and in the supercritical T > T , must remain finite. This suggests that the critical state of two coexisting homo-states within a c range T > Tc, must remain finite. This suggests that the critical state of two coexisting homo-states single Gibbs phase extends well into the supercritical region, and probably all the way to the Boyle within a single Gibbs phase extends well into the supercritical region, and probably all the way to the temperature as evidenced by the correlation of equation-of-state thermodynamic properties [28]. In the Boyle temperature as evidenced by the correlation of equation-of-state thermodynamic properties [28]. next section, we will re-assess the experimental evidence from historic laboratory measurements of In the next section, we will re-assess the experimental evidence from historic laboratory measurements near-critical and supercritical thermodynamic properties in the new light of the supercritical mesophase of near-critical and supercritical thermodynamic properties in the new light of the supercritical discovered in computer experiments. mesophase discovered in computer experiments. 2.3. Mesophase Dispersion 2.3. Mesophase Dispersion A colloidal dispersion is defined as one state, solid, liquid or gas, dispersed as small micro-scale A colloidal dispersion is defined as one state, solid, liquid or gas, dispersed as small micro-scale particles in a continuous state, also solid, liquid or gas. All well-characterised colloids hitherto comprise particles in a continuous state, also solid, liquid or gas. All well-characterised colloids hitherto at least 2 distinct chemical components, e.g., an emulsion of water in oil, or foam of air in water. comprise at least 2 distinct chemical components, e.g., an emulsion of water in oil, or foam of air in A dispersion of liquid in gas is a “mist”. We will see from the evidence reported below that there is water. A dispersion of liquid in gas is a “mist”. We will see from the evidence reported below that now every reason to believe that a fourth equilibrium state of a pure one-component thermodynamic there is now every reason to believe that a fourth equilibrium state of a pure one-component fluid system exists. The pre-percolation state can be considered a colloidal liquid-in-gas dispersion thermodynamic fluid system exists. The pre-percolation state can be considered a colloidal with the liquid state dispersed in the gas phase as very large clusters or hetero-phase fluctuations, liquid-in-gas dispersion with the liquid state dispersed in the gas phase as very large clusters or or gas-in-liquid vice versa. Within the mesophase both states percolate the phase volume. hetero-phase fluctuations, or gas-in-liquid vice versa. Within the mesophase both states percolate the The earliest experimental evidence for the existence of dispersed liquid at temperatures above phase volume. Tc can be found in the papers by Bradley et al. in 1908 [29]. Notwithstanding these results, in 1910 van der Waals gave his Nobel lecture [30] in which he ignored the Bradley et al. research with the declaration “at the critical volume the densities of gas and liquid become equal”. After exploring the effect of mechanical vibrations on the properties of near-critical CO2, however, Bradley et al. were able to state with some certainty that their experiments “proved” the existence of two phases far above the critical point. Moreover, their experimental observation that the meniscus disappears over a range of mean densities has never been properly explained. This reproducible experimental result, reviewed by cPDF Image | Supercritical Fluid Gaseous and Liquid States
PDF Search Title:
Supercritical Fluid Gaseous and Liquid StatesOriginal File Name Searched:
entropy-22-00437.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2 Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2. Gamma sulfur also known as mother of pearl sulfur and nacreous sulfur... More Info
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |