
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 054
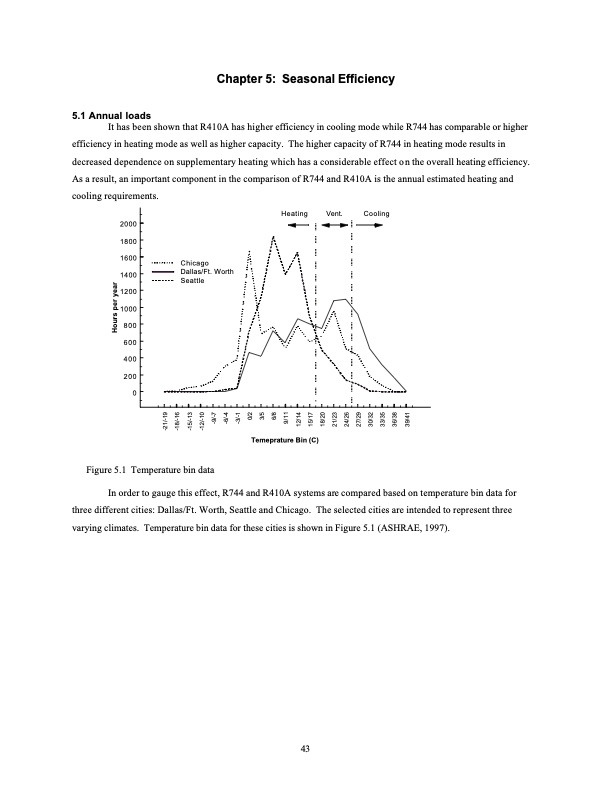
5.1 Annual loads Chapter 5: Seasonal Efficiency It has been shown that R410A has higher efficiency in cooling mode while R744 has comparable or higher efficiency in heating mode as well as higher capacity. The higher capacity of R744 in heating mode results in decreased dependence on supplementary heating which has a considerable effect on the overall heating efficiency. As a result, an important component in the comparison of R744 and R410A is the annual estimated heating and cooling requirements. 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 Figure 5.1 Temperature bin data Temeprature Bin (C) Heating Vent. Cooling Chicago Dallas/Ft. Worth Seattle In order to gauge this effect, R744 and R410A systems are compared based on temperature bin data for three different cities: Dallas/Ft. Worth, Seattle and Chicago. The selected cities are intended to represent three varying climates. Temperature bin data for these cities is shown in Figure 5.1 (ASHRAE, 1997). 43 -21/-19 -18/-16 -15/-13 -12/-10 -9/-7 -6/-4 -3/-1 0/2 3/5 6/8 9/11 12/14 15/17 18/20 21/23 24/26 27/29 30/32 33/35 36/38 39/41 Hours per yearPDF Image | Comparison of R744 and R410A
PDF Search Title:
Comparison of R744 and R410AOriginal File Name Searched:
CR039.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |