
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 011
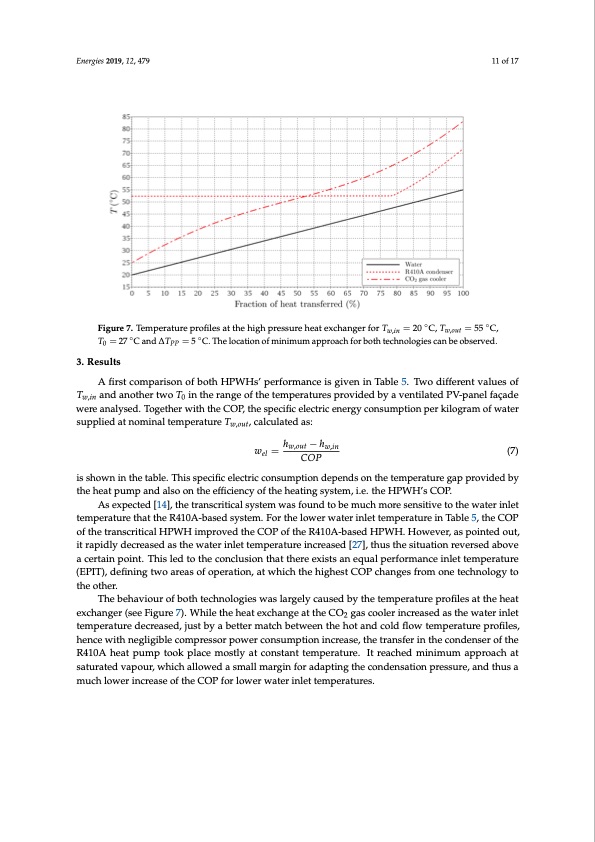
Energies 2019, 12, 479 11 of 17 Figure 7. Temperature profiles at the high pressure heat exchanger for Tw,in = 20 ◦C, Tw,out = 55 ◦C, T0 = 27 ◦C and ∆TPP = 5 ◦C. The location of minimum approach for both technologies can be observed. 3. Results A first comparison of both HPWHs’ performance is given in Table 5. Two different values of Tw,in and another two T0 in the range of the temperatures provided by a ventilated PV-panel façade were analysed. Together with the COP, the specific electric energy consumption per kilogram of water supplied at nominal temperature Tw,out, calculated as: wel = hw,out − hw,in (7) COP is shown in the table. This specific electric consumption depends on the temperature gap provided by the heat pump and also on the efficiency of the heating system, i.e. the HPWH’s COP. As expected [14], the transcritical system was found to be much more sensitive to the water inlet temperature that the R410A-based system. For the lower water inlet temperature in Table 5, the COP of the transcritical HPWH improved the COP of the R410A-based HPWH. However, as pointed out, it rapidly decreased as the water inlet temperature increased [27], thus the situation reversed above a certain point. This led to the conclusion that there exists an equal performance inlet temperature (EPIT), defining two areas of operation, at which the highest COP changes from one technology to the other. The behaviour of both technologies was largely caused by the temperature profiles at the heat exchanger (see Figure 7). While the heat exchange at the CO2 gas cooler increased as the water inlet temperature decreased, just by a better match between the hot and cold flow temperature profiles, hence with negligible compressor power consumption increase, the transfer in the condenser of the R410A heat pump took place mostly at constant temperature. It reached minimum approach at saturated vapour, which allowed a small margin for adapting the condensation pressure, and thus a much lower increase of the COP for lower water inlet temperatures.PDF Image | Comparison of Transcritical CO2 and Conventional Refrigerant Heat Pump
PDF Search Title:
Comparison of Transcritical CO2 and Conventional Refrigerant Heat PumpOriginal File Name Searched:
energies-12-00479.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |