
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 014
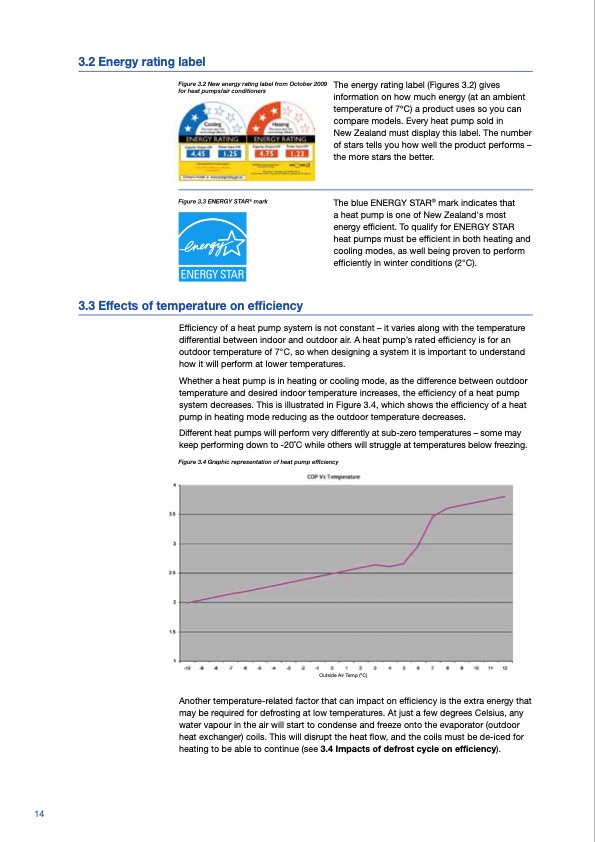
3.2 Energy rating label Figure 3.2 New energy rating label from October 2009 for heat pumps/air conditioners Figure 3.3 ENERGY STAR® mark 3.3 Effects of temperature on efficiency The energy rating label (Figures 3.2) gives information on how much energy (at an ambient temperature of 7oC) a product uses so you can compare models. Every heat pump sold in New Zealand must display this label. The number of stars tells you how well the product performs – the more stars the better. The blue ENERGY STAR® mark indicates that a heat pump is one of New Zealand's most energy efficient. To qualify for ENERGY STAR heat pumps must be efficient in both heating and cooling modes, as well being proven to perform efficiently in winter conditions (2°C). Efficiency of a heat pump system is not constant – it varies along with the temperature differential between indoor and outdoor air. A heat pump’s rated efficiency is for an outdoor temperature of 7°C, so when designing a system it is important to understand how it will perform at lower temperatures. Whether a heat pump is in heating or cooling mode, as the difference between outdoor temperature and desired indoor temperature increases, the efficiency of a heat pump system decreases. This is illustrated in Figure 3.4, which shows the efficiency of a heat pump in heating mode reducing as the outdoor temperature decreases. Different heat pumps will perform very differently at sub-zero temperatures – some may keep performing down to -20 ̊C while others will struggle at temperatures below freezing. Figure 3.4 Graphic representation of heat pump efficiency 14 Outside Air Temp (oC) Another temperature-related factor that can impact on efficiency is the extra energy that may be required for defrosting at low temperatures. At just a few degrees Celsius, any water vapour in the air will start to condense and freeze onto the evaporator (outdoor heat exchanger) coils. This will disrupt the heat flow, and the coils must be de-iced for heating to be able to continue (see 3.4 Impacts of defrost cycle on efficiency).PDF Image | Heat pump installation Good Practice Guide
PDF Search Title:
Heat pump installation Good Practice GuideOriginal File Name Searched:
Good_practice_heat_pump_installation.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |