
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 046
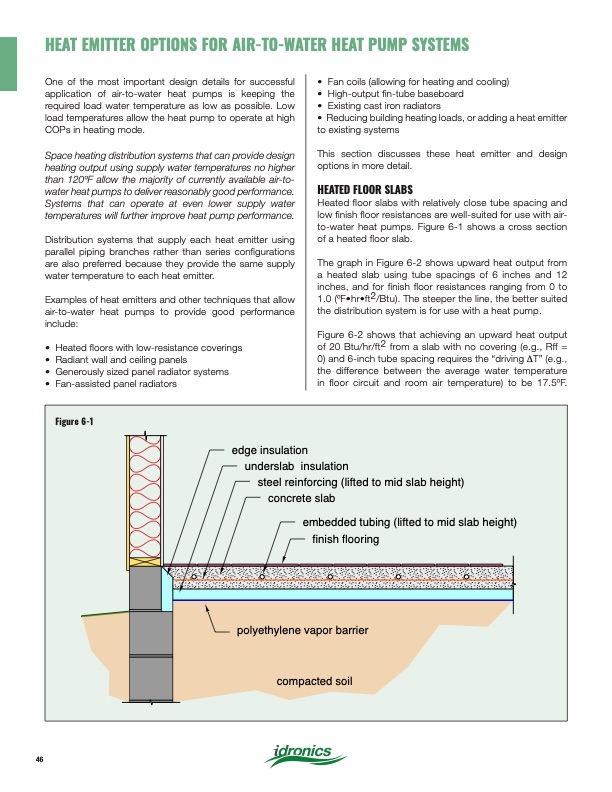
Figure 6-1 edge insulation underslab insulation steel reinforcing (lifted to mid slab height) concrete slab embedded tubing (lifted to mid slab height) finish flooring polyethylene vapor barrier compacted soil HEAT EMITTER OPTIONS FOR AIR-TO-WATER HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS One of the most important design details for successful application of air-to-water heat pumps is keeping the required load water temperature as low as possible. Low load temperatures allow the heat pump to operate at high COPs in heating mode. Space heating distribution systems that can provide design heating output using supply water temperatures no higher than 120oF allow the majority of currently available air-to- water heat pumps to deliver reasonably good performance. Systems that can operate at even lower supply water temperatures will further improve heat pump performance. Distribution systems that supply each heat emitter using parallel piping branches rather than series configurations are also preferred because they provide the same supply water temperature to each heat emitter. Examples of heat emitters and other techniques that allow air-to-water heat pumps to provide good performance include: • Heated floors with low-resistance coverings • Radiant wall and ceiling panels • Generously sized panel radiator systems • Fan-assisted panel radiators • Fan coils (allowing for heating and cooling) • High-output fin-tube baseboard • Existing cast iron radiators • Reducing building heating loads, or adding a heat emitter to existing systems This section discusses these heat emitter and design options in more detail. HEATED FLOOR SLABS Heated floor slabs with relatively close tube spacing and low finish floor resistances are well-suited for use with air- to-water heat pumps. Figure 6-1 shows a cross section of a heated floor slab. The graph in Figure 6-2 shows upward heat output from a heated slab using tube spacings of 6 inches and 12 inches, and for finish floor resistances ranging from 0 to 1.0 (oF•hr•ft2/Btu). The steeper the line, the better suited the distribution system is for use with a heat pump. Figure 6-2 shows that achieving an upward heat output of 20 Btu/hr/ft2 from a slab with no covering (e.g., Rff = 0) and 6-inch tube spacing requires the “driving ∆T” (e.g., the difference between the average water temperature in floor circuit and room air temperature) to be 17.5oF. 46PDF Image | Heat Pump Systems 2020
PDF Search Title:
Heat Pump Systems 2020Original File Name Searched:
idronics_27_na.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |