
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 027
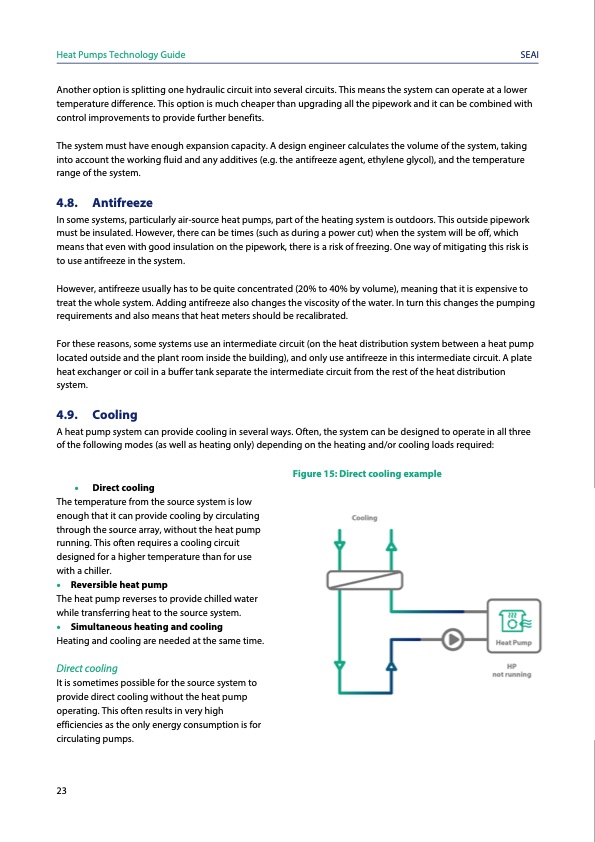
Heat Pumps Technology Guide SEAI Another option is splitting one hydraulic circuit into several circuits. This means the system can operate at a lower temperature difference. This option is much cheaper than upgrading all the pipework and it can be combined with control improvements to provide further benefits. The system must have enough expansion capacity. A design engineer calculates the volume of the system, taking into account the working fluid and any additives (e.g. the antifreeze agent, ethylene glycol), and the temperature range of the system. 4.8. Antifreeze In some systems, particularly air-source heat pumps, part of the heating system is outdoors. This outside pipework must be insulated. However, there can be times (such as during a power cut) when the system will be off, which means that even with good insulation on the pipework, there is a risk of freezing. One way of mitigating this risk is to use antifreeze in the system. However, antifreeze usually has to be quite concentrated (20% to 40% by volume), meaning that it is expensive to treat the whole system. Adding antifreeze also changes the viscosity of the water. In turn this changes the pumping requirements and also means that heat meters should be recalibrated. For these reasons, some systems use an intermediate circuit (on the heat distribution system between a heat pump located outside and the plant room inside the building), and only use antifreeze in this intermediate circuit. A plate heat exchanger or coil in a buffer tank separate the intermediate circuit from the rest of the heat distribution system. 4.9. Cooling A heat pump system can provide cooling in several ways. Often, the system can be designed to operate in all three of the following modes (as well as heating only) depending on the heating and/or cooling loads required: • Direct cooling The temperature from the source system is low enough that it can provide cooling by circulating through the source array, without the heat pump running. This often requires a cooling circuit designed for a higher temperature than for use with a chiller. • Reversible heat pump The heat pump reverses to provide chilled water while transferring heat to the source system. • Simultaneous heating and cooling Heating and cooling are needed at the same time. Direct cooling It is sometimes possible for the source system to provide direct cooling without the heat pump operating. This often results in very high efficiencies as the only energy consumption is for circulating pumps. Figure 15: Direct cooling example 23PDF Image | Heat Pumps Technology Guide
PDF Search Title:
Heat Pumps Technology GuideOriginal File Name Searched:
Heat-Pump-Technology-Guide.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |