
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 004
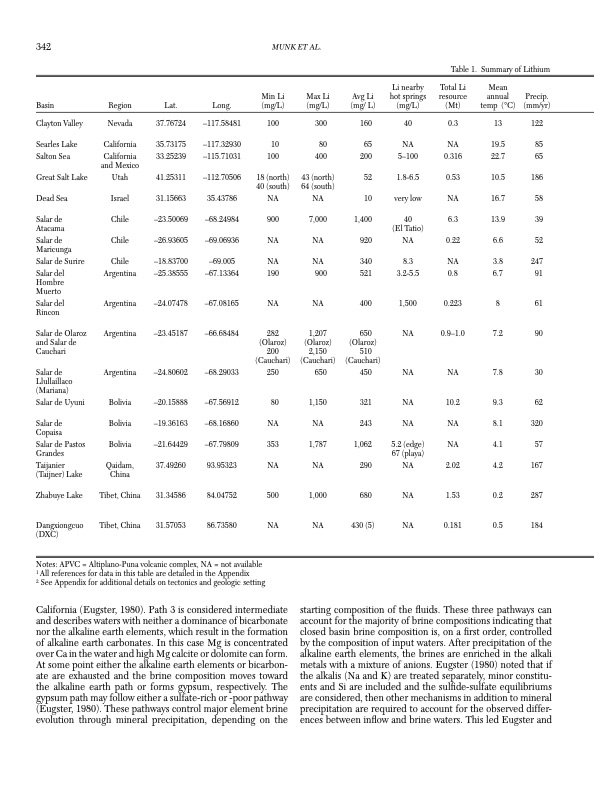
342 MUNK ET AL. 43 (north) 64 (south) NA 7,000 NA NA 900 NA 1,207 (Olaroz) 2,150 (Cauchari) (Cauchari) (Cauchari) 282 (Olaroz) 200 521 400 650 250 80 NA 353 NA 500 NA 650 1,150 NA 1,787 NA 1,000 NA 450 321 243 1,062 290 680 430 (5) (Olaroz) 510 Table 1. Summary of Lithium Mean annual Precip. temp (°C) (mm/yr) 40 0.3 13 122 Basin Region ClaytonValley Nevada SearlesLake California Lat. 37.76724 35.73175 33.25239 41.25311 31.15663 –23.50069 –26.93605 –18.83700 –25.38555 –24.07478 –23.45187 –24.80602 –20.15888 –19.36163 –21.64429 37.49260 31.34586 31.57053 Long. –117.58481 –117.32930 –115.71031 –112.70506 35.43786 –68.24984 –69.06936 –69.005 –67.13364 –67.08165 –66.68484 –68.29033 –67.56912 –68.16860 –67.79809 93.95323 84.04752 86.73580 Min Li Max Li (mg/L) (mg/L) 100 300 10 80 100 400 Avg Li (mg/ L) 160 65 200 52 10 1,400 920 340 Li nearby hot springs (mg/L) Total Li resource (Mt) Salton Sea Great Salt Lake Dead Sea Salar de Atacama Salar de Maricunga Salar de Surire Salar del Hombre Muerto Salar del Rincon Salar de Olaroz and Salar de Cauchari Salar de Llullaillaco (Mariana) Salar de Uyuni Salar de Copaisa Salar de Pastos Grandes Taijanier (Taijner) Lake Zhabuye Lake Dangxiongcuo (DXC) California and Mexico Utah Israel Chile Chile Chile Argentina Argentina Argentina Argentina Bolivia Bolivia Bolivia Qaidam, China Tibet, China Tibet, China 18 (north) 40 (south) NA 900 NA NA 190 NA NA NA 5–100 0.316 1.8‐6.5 0.53 very low NA 40 6.3 (El Tatio) NA 0.22 8.3 NA 3.2‐5.5 0.8 1,500 0.223 NA 0.9–1.0 NA NA NA 10.2 NA NA 5.2 (edge) NA 67 (playa) NA 2.02 NA 1.53 NA 0.181 19.5 85 22.7 65 10.5 186 16.7 58 13.9 39 6.6 52 3.8 247 6.7 91 8 61 7.2 90 7.8 30 9.3 62 8.1 320 4.1 57 4.2 167 0.2 287 0.5 184 Notes: APVC = Altiplano‐Puna volcanic complex, NA = not available 1 All references for data in this table are detailed in the Appendix 2 See Appendix for additional details on tectonics and geologic setting California (Eugster, 1980). Path 3 is considered intermediate and describes waters with neither a dominance of bicarbonate nor the alkaline earth elements, which result in the formation of alkaline earth carbonates. In this case Mg is concentrated over Ca in the water and high Mg calcite or dolomite can form. At some point either the alkaline earth elements or bicarbon- ate are exhausted and the brine composition moves toward the alkaline earth path or forms gypsum, respectively. The gypsum path may follow either a sulfate‐rich or -poor pathway (Eugster, 1980). These pathways control major element brine evolution through mineral precipitation, depending on the starting composition of the fluids. These three pathways can account for the majority of brine compositions indicating that closed basin brine composition is, on a first order, controlled by the composition of input waters. After precipitation of the alkaline earth elements, the brines are enriched in the alkali metals with a mixture of anions. Eugster (1980) noted that if the alkalis (Na and K) are treated separately, minor constitu- ents and Si are included and the sulfide‐sulfate equilibriums are considered, then other mechanisms in addition to mineral precipitation are required to account for the observed differ- ences between inflow and brine waters. This led Eugster andPDF Image | Lithium Brines A Global Perspective
PDF Search Title:
Lithium Brines A Global PerspectiveOriginal File Name Searched:
14_Munketal.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Product and Development Focus for Infinity Turbine
ORC Waste Heat Turbine and ORC System Build Plans: All turbine plans are $10,000 each. This allows you to build a system and then consider licensing for production after you have completed and tested a unit.Redox Flow Battery Technology: With the advent of the new USA tax credits for producing and selling batteries ($35/kW) we are focussing on a simple flow battery using shipping containers as the modular electrolyte storage units with tax credits up to $140,000 per system. Our main focus is on the salt battery. This battery can be used for both thermal and electrical storage applications. We call it the Cogeneration Battery or Cogen Battery. One project is converting salt (brine) based water conditioners to simultaneously produce power. In addition, there are many opportunities to extract Lithium from brine (salt lakes, groundwater, and producer water).Salt water or brine are huge sources for lithium. Most of the worlds lithium is acquired from a brine source. It's even in seawater in a low concentration. Brine is also a byproduct of huge powerplants, which can now use that as an electrolyte and a huge flow battery (which allows storage at the source).We welcome any business and equipment inquiries, as well as licensing our turbines for manufacturing.| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |