
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 012
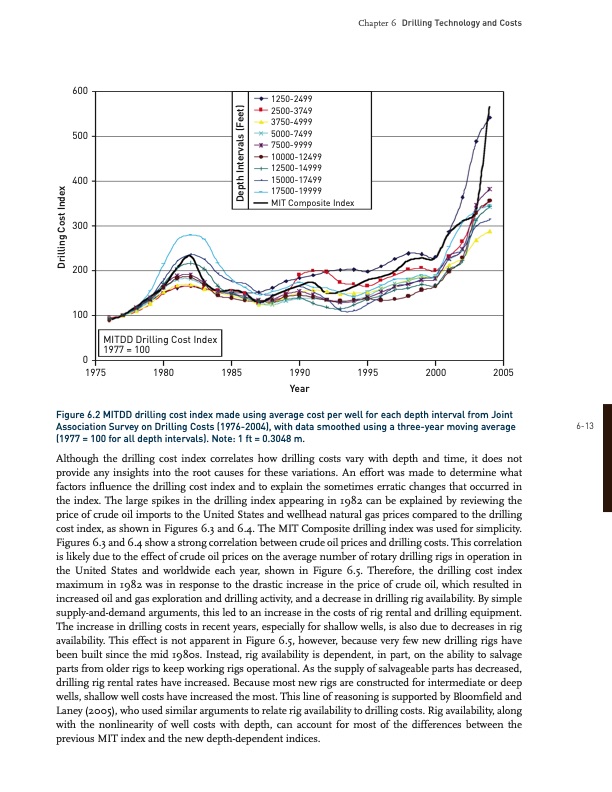
600 500 400 15000-17499 Drilling Technology and Costs 300 17500-19999 MIT Composite Index 1250-2499 2500-3749 3750-4999 5000-7499 7500-9999 10000-12499 12500-14999 200 100 MITDD Drilling Cost Index 1977 = 100 Chapter 6 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 Year Figure 6.2 MITDD drilling cost index made using average cost per well for each depth interval from Joint Association Survey on Drilling Costs (19762004), with data smoothed using a threeyear moving average 613 (1977 = 100 for all depth intervals). Note: 1 ft = 0.3048 m. Although the drilling cost index correlates how drilling costs vary with depth and time, it does not provide any insights into the root causes for these variations. An effort was made to determine what factors influence the drilling cost index and to explain the sometimes erratic changes that occurred in the index. The large spikes in the drilling index appearing in 1982 can be explained by reviewing the price of crude oil imports to the United States and wellhead natural gas prices compared to the drilling cost index, as shown in Figures 6.3 and 6.4. The MIT Composite drilling index was used for simplicity. Figures 6.3 and 6.4 show a strong correlation between crude oil prices and drilling costs. This correlation is likely due to the effect of crude oil prices on the average number of rotary drilling rigs in operation in the United States and worldwide each year, shown in Figure 6.5. Therefore, the drilling cost index maximum in 1982 was in response to the drastic increase in the price of crude oil, which resulted in increased oil and gas exploration and drilling activity, and a decrease in drilling rig availability. By simple supplyanddemand arguments, this led to an increase in the costs of rig rental and drilling equipment. The increase in drilling costs in recent years, especially for shallow wells, is also due to decreases in rig availability. This effect is not apparent in Figure 6.5, however, because very few new drilling rigs have been built since the mid 1980s. Instead, rig availability is dependent, in part, on the ability to salvage parts from older rigs to keep working rigs operational. As the supply of salvageable parts has decreased, drilling rig rental rates have increased. Because most new rigs are constructed for intermediate or deep wells, shallow well costs have increased the most. This line of reasoning is supported by Bloomfield and Laney (2005), who used similar arguments to relate rig availability to drilling costs. Rig availability, along with the nonlinearity of well costs with depth, can account for most of the differences between the previous MIT index and the new depthdependent indices. Drilling Cost Index Depth Intervals (Feet)PDF Image | Drilling Technology and Costs
PDF Search Title:
Drilling Technology and CostsOriginal File Name Searched:
egs_chapter_6.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
NFT (Non Fungible Token): Buy our tech, design, development or system NFT and become part of our tech NFT network... More Info
IT XR Project Redstone NFT Available for Sale: NFT for high tech turbine design with one part 3D printed counter-rotating energy turbine. Be part of the future with this NFT. Can be bought and sold but only one design NFT exists. Royalties go to the developer (Infinity) to keep enhancing design and applications... More Info
Infinity Turbine IT XR Project Redstone Design: NFT for sale... NFT for high tech turbine design with one part 3D printed counter-rotating energy turbine. Includes all rights to this turbine design, including license for Fluid Handling Block I and II for the turbine assembly and housing. The NFT includes the blueprints (cad/cam), revenue streams, and all future development of the IT XR Project Redstone... More Info
Infinity Turbine ROT Radial Outflow Turbine 24 Design and Worldwide Rights: NFT for sale... NFT for the ROT 24 energy turbine. Be part of the future with this NFT. This design can be bought and sold but only one design NFT exists. You may manufacture the unit, or get the revenues from its sale from Infinity Turbine. Royalties go to the developer (Infinity) to keep enhancing design and applications... More Info
Infinity Supercritical CO2 10 Liter Extractor Design and Worldwide Rights: The Infinity Supercritical 10L CO2 extractor is for botanical oil extraction, which is rich in terpenes and can produce shelf ready full spectrum oil. With over 5 years of development, this industry leader mature extractor machine has been sold since 2015 and is part of many profitable businesses. The process can also be used for electrowinning, e-waste recycling, and lithium battery recycling, gold mining electronic wastes, precious metals. CO2 can also be used in a reverse fuel cell with nafion to make a gas-to-liquids fuel, such as methanol, ethanol and butanol or ethylene. Supercritical CO2 has also been used for treating nafion to make it more effective catalyst. This NFT is for the purchase of worldwide rights which includes the design. More Info
NFT (Non Fungible Token): Buy our tech, design, development or system NFT and become part of our tech NFT network... More Info
Infinity Turbine Products: Special for this month, any plans are $10,000 for complete Cad/Cam blueprints. License is for one build. Try before you buy a production license. May pay by Bitcoin or other Crypto. Products Page... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |