
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 038
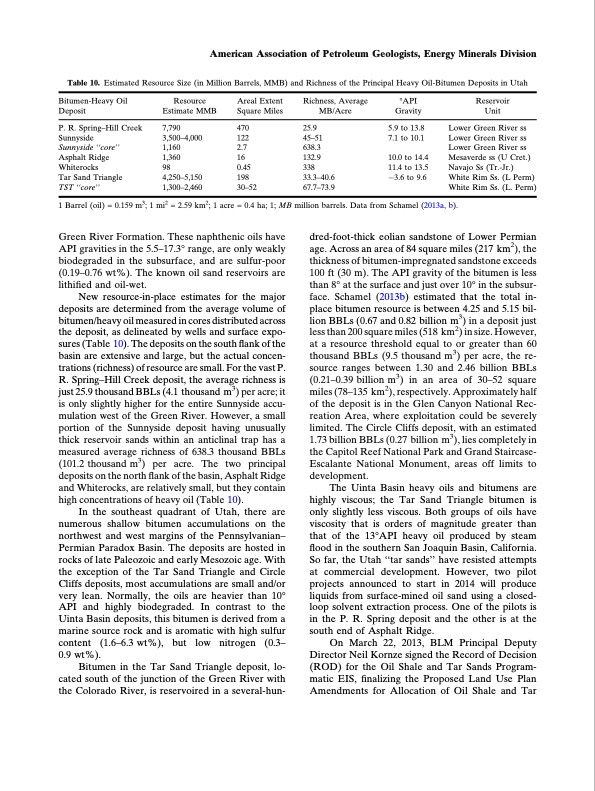
American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Energy Minerals Division Table 10. Estimated Resource Size (in Million Barrels, MMB) and Richness of the Principal Heavy Oil-Bitumen Deposits in Utah Bitumen-Heavy Oil Deposit P. R. Spring–Hill Creek Sunnyside Sunnyside ‘‘core’’ Asphalt Ridge Whiterocks Tar Sand Triangle TST ‘‘core’’ Resource Estimate MMB 7,790 3,500–4,000 1,160 1,360 98 4,250–5,150 1,300–2,460 Areal Extent Square Miles 470 122 2.7 16 0.45 198 30–52 Richness, Average MB/Acre 25.9 45–51 638.3 132.9 338 33.3–40.6 67.7–73.9 °API Gravity 5.9 to 13.8 7.1 to 10.1 10.0 to 14.4 11.4 to 13.5 3.6 to 9.6 Reservoir Unit Lower Green River ss Lower Green River ss Lower Green River ss Mesaverde ss (U Cret.) Navajo Ss (Tr.-Jr.) White Rim Ss. (L Perm) White Rim Ss. (L. Perm) 1 Barrel (oil) = 0.159 m3; 1 mi2 = 2.59 km2; 1 acre = 0.4 ha; 1; MB million barrels. Data from Schamel (2013a, b). Green River Formation. These naphthenic oils have API gravities in the 5.5–17.3° range, are only weakly biodegraded in the subsurface, and are sulfur-poor (0.19–0.76 wt%). The known oil sand reservoirs are lithified and oil-wet. New resource-in-place estimates for the major deposits are determined from the average volume of bitumen/heavy oil measured in cores distributed across the deposit, as delineated by wells and surface expo- sures (Table 10). The deposits on the south flank of the basin are extensive and large, but the actual concen- trations (richness) of resource are small. For the vast P. R. Spring–Hill Creek deposit, the average richness is just 25.9 thousand BBLs (4.1 thousand m3) per acre; it is only slightly higher for the entire Sunnyside accu- mulation west of the Green River. However, a small portion of the Sunnyside deposit having unusually thick reservoir sands within an anticlinal trap has a measured average richness of 638.3 thousand BBLs (101.2 thousand m3) per acre. The two principal deposits on the north flank of the basin, Asphalt Ridge and Whiterocks, are relatively small, but they contain high concentrations of heavy oil (Table 10). In the southeast quadrant of Utah, there are numerous shallow bitumen accumulations on the northwest and west margins of the Pennsylvanian– Permian Paradox Basin. The deposits are hosted in rocks of late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic age. With the exception of the Tar Sand Triangle and Circle Cliffs deposits, most accumulations are small and/or very lean. Normally, the oils are heavier than 10° API and highly biodegraded. In contrast to the Uinta Basin deposits, this bitumen is derived from a marine source rock and is aromatic with high sulfur content (1.6–6.3 wt%), but low nitrogen (0.3– 0.9 wt%). Bitumen in the Tar Sand Triangle deposit, lo- cated south of the junction of the Green River with the Colorado River, is reservoired in a several-hun- dred-foot-thick eolian sandstone of Lower Permian age. Across an area of 84 square miles (217 km2), the thickness of bitumen-impregnated sandstone exceeds 100 ft (30 m). The API gravity of the bitumen is less than 8° at the surface and just over 10° in the subsur- face. Schamel (2013b) estimated that the total in- place bitumen resource is between 4.25 and 5.15 bil- lion BBLs (0.67 and 0.82 billion m3) in a deposit just less than 200 square miles (518 km2) in size. However, at a resource threshold equal to or greater than 60 thousand BBLs (9.5 thousand m3) per acre, the re- source ranges between 1.30 and 2.46 billion BBLs (0.21–0.39 billion m3) in an area of 30–52 square miles (78–135 km2), respectively. Approximately half of the deposit is in the Glen Canyon National Rec- reation Area, where exploitation could be severely limited. The Circle Cliffs deposit, with an estimated 1.73 billion BBLs (0.27 billion m3), lies completely in the Capitol Reef National Park and Grand Staircase- Escalante National Monument, areas off limits to development. The Uinta Basin heavy oils and bitumens are highly viscous; the Tar Sand Triangle bitumen is only slightly less viscous. Both groups of oils have viscosity that is orders of magnitude greater than that of the 13°API heavy oil produced by steam flood in the southern San Joaquin Basin, California. So far, the Utah ‘‘tar sands’’ have resisted attempts at commercial development. However, two pilot projects announced to start in 2014 will produce liquids from surface-mined oil sand using a closed- loop solvent extraction process. One of the pilots is in the P. R. Spring deposit and the other is at the south end of Asphalt Ridge. On March 22, 2013, BLM Principal Deputy Director Neil Kornze signed the Record of Decision (ROD) for the Oil Shale and Tar Sands Program- matic EIS, finalizing the Proposed Land Use Plan Amendments for Allocation of Oil Shale and TarPDF Image | Unconventional Energy Resources
PDF Search Title:
Unconventional Energy ResourcesOriginal File Name Searched:
EMD_AAPG_2013_NRR_online.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
NFT (Non Fungible Token): Buy our tech, design, development or system NFT and become part of our tech NFT network... More Info
IT XR Project Redstone NFT Available for Sale: NFT for high tech turbine design with one part 3D printed counter-rotating energy turbine. Be part of the future with this NFT. Can be bought and sold but only one design NFT exists. Royalties go to the developer (Infinity) to keep enhancing design and applications... More Info
Infinity Turbine IT XR Project Redstone Design: NFT for sale... NFT for high tech turbine design with one part 3D printed counter-rotating energy turbine. Includes all rights to this turbine design, including license for Fluid Handling Block I and II for the turbine assembly and housing. The NFT includes the blueprints (cad/cam), revenue streams, and all future development of the IT XR Project Redstone... More Info
Infinity Turbine ROT Radial Outflow Turbine 24 Design and Worldwide Rights: NFT for sale... NFT for the ROT 24 energy turbine. Be part of the future with this NFT. This design can be bought and sold but only one design NFT exists. You may manufacture the unit, or get the revenues from its sale from Infinity Turbine. Royalties go to the developer (Infinity) to keep enhancing design and applications... More Info
Infinity Supercritical CO2 10 Liter Extractor Design and Worldwide Rights: The Infinity Supercritical 10L CO2 extractor is for botanical oil extraction, which is rich in terpenes and can produce shelf ready full spectrum oil. With over 5 years of development, this industry leader mature extractor machine has been sold since 2015 and is part of many profitable businesses. The process can also be used for electrowinning, e-waste recycling, and lithium battery recycling, gold mining electronic wastes, precious metals. CO2 can also be used in a reverse fuel cell with nafion to make a gas-to-liquids fuel, such as methanol, ethanol and butanol or ethylene. Supercritical CO2 has also been used for treating nafion to make it more effective catalyst. This NFT is for the purchase of worldwide rights which includes the design. More Info
NFT (Non Fungible Token): Buy our tech, design, development or system NFT and become part of our tech NFT network... More Info
Infinity Turbine Products: Special for this month, any plans are $10,000 for complete Cad/Cam blueprints. License is for one build. Try before you buy a production license. May pay by Bitcoin or other Crypto. Products Page... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |