
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 003
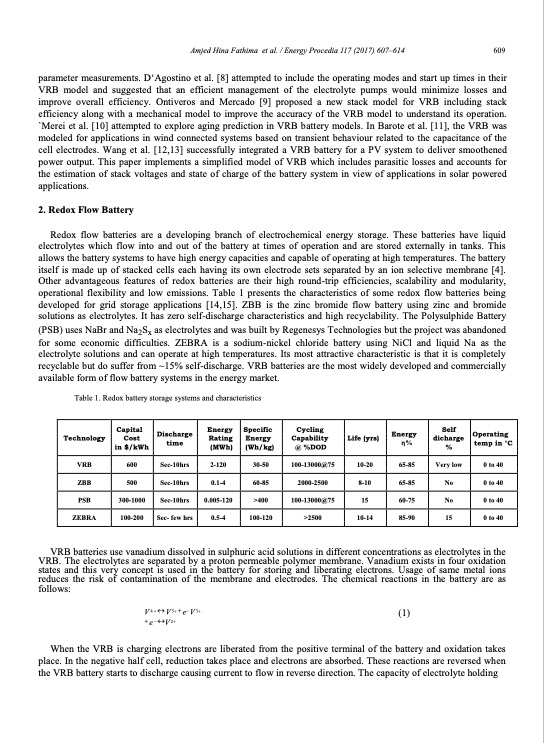
Amjed Hina Fathima et al. / Energy Procedia 117 (2017) 607–614 609 Fathima AH and Palanisamy K/ Energy Procedia 00 (2017) 000–000 3 parameter measurements. D‘Agostino et al. [8] attempted to include the operating modes and start up times in their VRB model and suggested that an efficient management of the electrolyte pumps would minimize losses and improve overall efficiency. Ontiveros and Mercado [9] proposed a new stack model for VRB including stack efficiency along with a mechanical model to improve the accuracy of the VRB model to understand its operation. `Merei et al. [10] attempted to explore aging prediction in VRB battery models. In Barote et al. [11], the VRB was modeled for applications in wind connected systems based on transient behaviour related to the capacitance of the cell electrodes. Wang et al. [12,13] successfully integrated a VRB battery for a PV system to deliver smoothened power output. This paper implements a simplified model of VRB which includes parasitic losses and accounts for the estimation of stack voltages and state of charge of the battery system in view of applications in solar powered applications. 2. Redox Flow Battery Redox flow batteries are a developing branch of electrochemical energy storage. These batteries have liquid electrolytes which flow into and out of the battery at times of operation and are stored externally in tanks. This allows the battery systems to have high energy capacities and capable of operating at high temperatures. The battery itself is made up of stacked cells each having its own electrode sets separated by an ion selective membrane [4]. Other advantageous features of redox batteries are their high round-trip efficiencies, scalability and modularity, operational flexibility and low emissions. Table 1 presents the characteristics of some redox flow batteries being developed for grid storage applications [14,15]. ZBB is the zinc bromide flow battery using zinc and bromide solutions as electrolytes. It has zero self-discharge characteristics and high recyclability. The Polysulphide Battery (PSB) uses NaBr and Na2Sx as electrolytes and was built by Regenesys Technologies but the project was abandoned for some economic difficulties. ZEBRA is a sodium-nickel chloride battery using NiCl and liquid Na as the electrolyte solutions and can operate at high temperatures. Its most attractive characteristic is that it is completely recyclable but do suffer from ~15% self-discharge. VRB batteries are the most widely developed and commercially available form of flow battery systems in the energy market. Table 1. Redox battery storage systems and characteristics Capital Technology Cost in $/kWh Discharge time Energy Rating (MWh) Specific Energy (Wh/kg) Cycling Capability @ %DOD Life (yrs) Energy η% 65-85 65-85 60-75 85-90 Self dicharge % Very low No No 15 Operating temp in °C 0 to 40 0 to 40 0 to 40 0 to 40 VRB 600 Sec-10hrs 2-120 30-50 100-13000@75 10-20 ZBB PSB ZEBRA 500 300-1000 100-200 Sec-10hrs Sec-10hrs Sec- few hrs 0.1-4 0.005-120 0.5-4 60-85 >400 100-120 2000-2500 100-13000@75 >2500 8-10 15 10-14 VRB batteries use vanadium dissolved in sulphuric acid solutions in different concentrations as electrolytes in the VRB. The electrolytes are separated by a proton permeable polymer membrane. Vanadium exists in four oxidation states and this very concept is used in the battery for storing and liberating electrons. Usage of same metal ions reduces the risk of contamination of the membrane and electrodes. The chemical reactions in the battery are as follows: V4 V5 e V3 (1) e V 2 When the VRB is charging electrons are liberated from the positive terminal of the battery and oxidation takes place. In the negative half cell, reduction takes place and electrons are absorbed. These reactions are reversed when the VRB battery starts to discharge causing current to flow in reverse direction. The capacity of electrolyte holdingPDF Image | Operation of a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery for PV
PDF Search Title:
Operation of a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery for PVOriginal File Name Searched:
S1876610217323834-main.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Salgenx Redox Flow Battery Technology: Salt water flow battery technology with low cost and great energy density that can be used for power storage and thermal storage. Let us de-risk your production using our license. Our aqueous flow battery is less cost than Tesla Megapack and available faster. Redox flow battery. No membrane needed like with Vanadium, or Bromine. Salgenx flow battery
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@salgenx.com | RSS | AMP |