
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 002
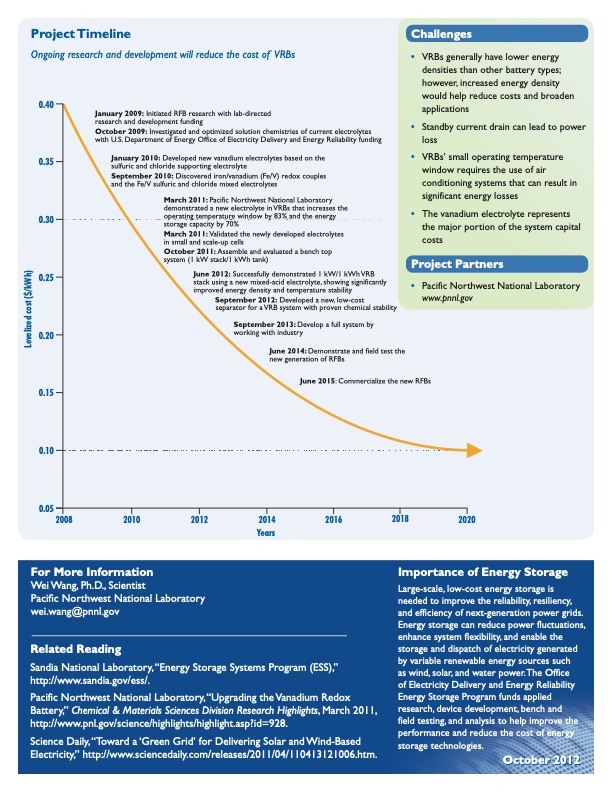
Project Timeline Ongoing research and development will reduce the cost of VRBs Challenges • VRBs generally have lower energy densities than other battery types; however, increased energy density would help reduce costs and broaden applications • Standby current drain can lead to power loss • VRBs’ small operating temperature window requires the use of air conditioning systems that can result in significant energy losses • The vanadium electrolyte represents the major portion of the system capital costs Project Partners • Pacific Northwest National Laboratory www.pnnl.gov 0.40 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 January 2009: Initiated RFB research with lab-directed research and development funding October 2009: Investigated and optimized solution chemistries of current electrolytes with U.S. Department of Energy Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability funding January 2010: Developed new vanadium electrolytes based on the sulfuric and chloride supporting electrolyte September 2010: Discovered iron/vanadium (Fe/V) redox couples and the Fe/V sulfuric and chloride mixed electrolytes March 2011: Pacific Northwest National Laboratory demonstrated a new electrolyte in VRBs that increases the operating temperature window by 83% and the energy storage capacity by 70% March 2011: Validated the newly developed electrolytes in small and scale-up cells October 2011: Assemble and evaluated a bench top system (1 kW stack/1 kWh tank) June 2012: Successfully demonstrated 1 kW/1 kWh VRB stack using a new mixed-acid electrolyte, showing significantly improved energy density and temperature stability September 2012: Developed a new, low-cost separator for a VRB system with proven chemical stability September 2013: Develop a full system by working with industry June 2014: Demonstrate and field test the new generation of RFBs Levelized cost ($/kWh) 2008 2010 2012 2014 Years 2016 2018 2020 Importance of Energy Storage Large-scale, low-cost energy storage is needed to improve the reliability, resiliency, and efficiency of next-generation power grids. Energy storage can reduce power fluctuations, enhance system flexibility, and enable the storage and dispatch of electricity generated by variable renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and water power.The Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability Energy Storage Program funds applied research, device development, bench and field testing, and analysis to help improve the performance and reduce the cost of energy storage technologies. October 2012 For More Information Wei Wang, Ph.D., Scientist Pacific Northwest National Laboratory wei.wang@pnnl.gov Related Reading Sandia National Laboratory,“Energy Storage Systems Program (ESS),” http://www.sandia.gov/ess/. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory,“Upgrading theVanadium Redox Battery,” Chemical & Materials Sciences Division Research Highlights, March 2011, http://www.pnl.gov/science/highlights/highlight.asp?id=928. Science Daily,“Toward a‘Green Grid’ for Delivering Solar andWind-Based Electricity,” http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2011/04/110413121006.htm. June 2015: Commercialize the new RFBsPDF Image | Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries USDOE
PDF Search Title:
Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries USDOEOriginal File Name Searched:
081_Vanadium_Redox_Battieries.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Salgenx Redox Flow Battery Technology: Salt water flow battery technology with low cost and great energy density that can be used for power storage and thermal storage. Let us de-risk your production using our license. Our aqueous flow battery is less cost than Tesla Megapack and available faster. Redox flow battery. No membrane needed like with Vanadium, or Bromine. Salgenx flow battery
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@salgenx.com | RSS | AMP |