
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 006
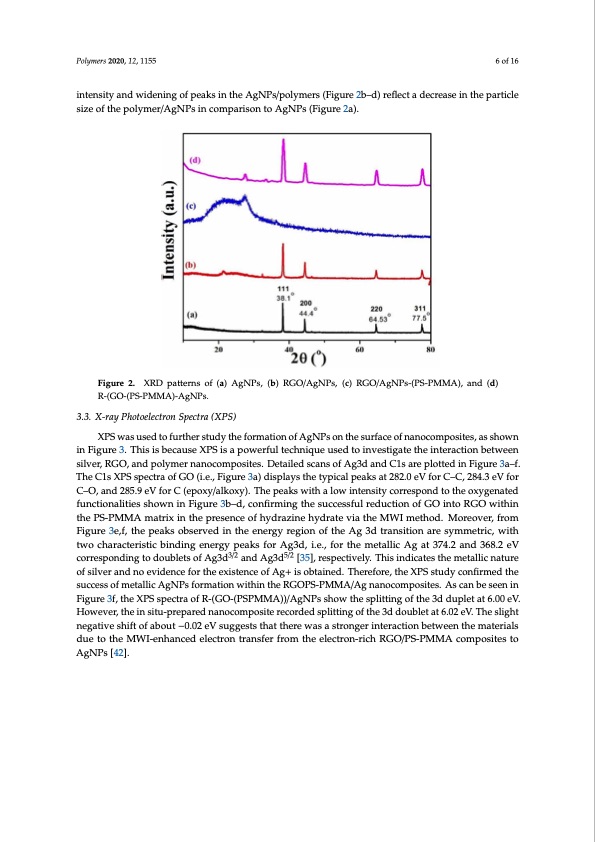
Polymers 2020, 12, 1155 6 of 16 intensity and widening of peaks in the AgNPs/polymers (Figure 2b–d) reflect a decrease in the particle size of the polymer/AgNPs in comparison to AgNPs (Figure 2a). Polymers 2020, 12, x FOR PEER REVIEW 6 of 16 Figure 2. XRD patterns of (a) AgNPs, (b) RGO/AgNPs, (c) RGO/AgNPs-(PS-PMMA), and (d) R-(GO- Figure 2. XRD patterns of (a) AgNPs, (b) RGO/AgNPs, (c) RGO/AgNPs-(PS-PMMA), and (d) (PS-PMMA)-AgNPs. R-(GO-(PS-PMMA)-AgNPs. 3.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectra (XPS) 3.3. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectra (XPS) XPS was used to further study the formation of AgNPs on the surface of nanocomposites, as shown XPS was used to further study the formation of AgNPs on the surface of nanocomposites, as in Figure 3. This is because XPS is a powerful technique used to investigate the interaction between shown in Figure 3. This is because XPS is a powerful technique used to investigate the interaction silver, RGO, and polymer nanocomposites. Detailed scans of Ag3d and C1s are plotted in Figure 3a–f. between silver, RGO, and polymer nanocomposites. Detailed scans of Ag3d and C1s are plotted in The C1s XPS spectra of GO (i.e., Figure 3a) displays the typical peaks at 282.0 eV for C–C, 284.3 eV for Figure 3a–f. The C1s XPS spectra of GO (i.e., Figure 3a) displays the typical peaks at 282.0 eV for C– C–O, and 285.9 eV for C (epoxy/alkoxy). The peaks with a low intensity correspond to the oxygenated C, 284.3 eV for C–O, and 285.9 eV for C (epoxy/alkoxy). The peaks with a low intensity correspond functionalities shown in Figure 3b–d, confirming the successful reduction of GO into RGO within to the oxygenated functionalities shown in Figure 3b–d, confirming the successful reduction of GO the PS-PMMA matrix in the presence of hydrazine hydrate via the MWI method. Moreover, from into RGO within the PS-PMMA matrix in the presence of hydrazine hydrate via the MWI method. Figure 3e,f, the peaks observed in the energy region of the Ag 3d transition are symmetric, with Moreover, from Figure 3e,f, the peaks observed in the energy region of the Ag 3d transition are two characteristic binding energy peaks for Ag3d, i.e., for the metallic Ag at 374.2 and 368.2 eV symmetric, with two characteristic binding energy peaks for Ag3d, i.e., for the metallic Ag at 374.2 corresponding to doublets of Ag3d3/2 and Ag3d5/2 [33/25], respectiv5/2ely. This indicates the metallic nature and 368.2 eV corresponding to doublets of Ag3d and Ag3d [35], respectively. This indicates the of silver and no evidence for the existence of Ag+ is obtained. Therefore, the XPS study confirmed the metallic nature of silver and no evidence for the existence of Ag+ is obtained. Therefore, the XPS success of metallic AgNPs formation within the RGOPS-PMMA/Ag nanocomposites. As can be seen in study confirmed the success of metallic AgNPs formation within the RGOPS-PMMA/Ag Figure 3f, the XPS spectra of R-(GO-(PSPMMA))/AgNPs show the splitting of the 3d duplet at 6.00 eV. nanocomposites. As can be seen in Figure 3f, the XPS spectra of R-(GO-(PSPMMA))/AgNPs show the However, the in situ-prepared nanocomposite recorded splitting of the 3d doublet at 6.02 eV. The slight splitting of the 3d duplet at 6.00 eV. However, the in situ-prepared nanocomposite recorded splitting negative shift of about −0.02 eV suggests that there was a stronger interaction between the materials of the 3d doublet at 6.02 eV. The slight negative shift of about - 0.02 eV suggests that there was a due to the MWI-enhanced electron transfer from the electron-rich RGO/PS-PMMA composites to stronger interaction between the materials due to the MWI-enhanced electron transfer from the AgNPs [42]. electron-rich RGO/PS-PMMA composites to AgNPs [42].PDF Image | Microwave Irradiation Synthesis Silver Nanoparticle
PDF Search Title:
Microwave Irradiation Synthesis Silver NanoparticleOriginal File Name Searched:
polymers-12-01155-v2.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Turbine and System Plans CAD CAM: Special for this month, any plans are $10,000 for complete Cad/Cam blueprints. License is for one build. Try before you buy a production license. More Info
Waste Heat Power Technology: Organic Rankine Cycle uses waste heat to make electricity, shaft horsepower and cooling. More Info
All Turbine and System Products: Infinity Turbine ORD systems, turbine generator sets, build plans and more to use your waste heat from 30C to 100C. More Info
CO2 Phase Change Demonstrator: CO2 goes supercritical at 30 C. This is a experimental platform which you can use to demonstrate phase change with low heat. Includes integration area for small CO2 turbine, static generator, and more. This can also be used for a GTL Gas to Liquids experimental platform. More Info
Introducing the Infinity Turbine Products Infinity Turbine develops and builds systems for making power from waste heat. It also is working on innovative strategies for storing, making, and deploying energy. More Info
Need Strategy? Use our Consulting and analyst services Infinity Turbine LLC is pleased to announce its consulting and analyst services. We have worked in the renewable energy industry as a researcher, developing sales and markets, along with may inventions and innovations. More Info
Made in USA with Global Energy Millennial Web Engine These pages were made with the Global Energy Web PDF Engine using Filemaker (Claris) software.
Infinity Turbine Developing Spinning Disc Reactor SDR or Spinning Disc Reactors reduce processing time for liquid production of Silver Nanoparticles.
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |