
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 005
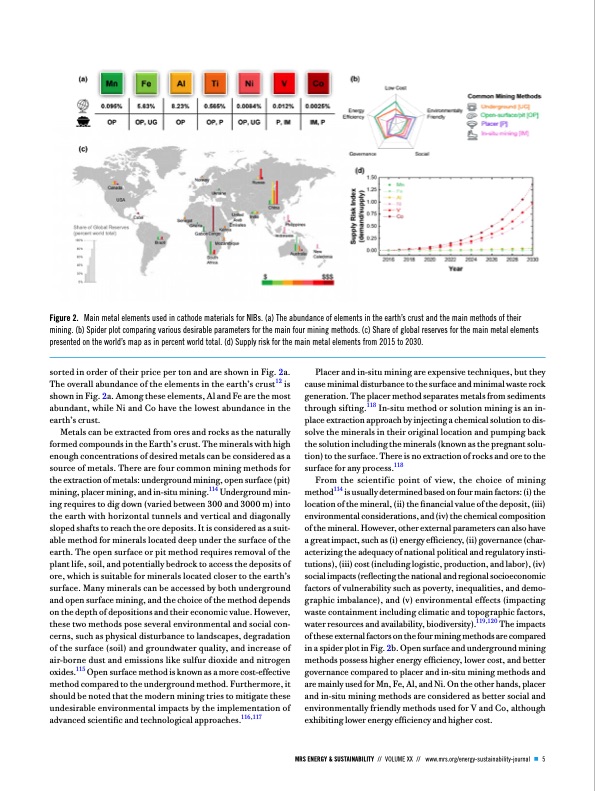
Figure 2. Main metal elements used in cathode materials for NIBs. (a) The abundance of elements in the earth’s crust and the main methods of their mining. (b) Spider plot comparing various desirable parameters for the main four mining methods. (c) Share of global reserves for the main metal elements presented on the world’s map as in percent world total. (d) Supply risk for the main metal elements from 2015 to 2030. sorted in order of their price per ton and are shown in Fig. 2a. The overall abundance of the elements in the earth’s crust12 is shown in Fig. 2a. Among these elements, Al and Fe are the most abundant, while Ni and Co have the lowest abundance in the earth’s crust. Metals can be extracted from ores and rocks as the naturally formed compounds in the Earth’s crust. The minerals with high enough concentrations of desired metals can be considered as a source of metals. There are four common mining methods for the extraction of metals: underground mining, open surface (pit) mining, placer mining, and in-situ mining.114 Underground min- ing requires to dig down (varied between 300 and 3000 m) into the earth with horizontal tunnels and vertical and diagonally sloped shafts to reach the ore deposits. It is considered as a suit- able method for minerals located deep under the surface of the earth. The open surface or pit method requires removal of the plant life, soil, and potentially bedrock to access the deposits of ore, which is suitable for minerals located closer to the earth’s surface. Many minerals can be accessed by both underground and open surface mining, and the choice of the method depends on the depth of depositions and their economic value. However, these two methods pose several environmental and social con- cerns, such as physical disturbance to landscapes, degradation of the surface (soil) and groundwater quality, and increase of air-borne dust and emissions like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.115 Open surface method is known as a more cost-effective method compared to the underground method. Furthermore, it should be noted that the modern mining tries to mitigate these undesirable environmental impacts by the implementation of advanced scientific and technological approaches.116,117 Placer and in-situ mining are expensive techniques, but they cause minimal disturbance to the surface and minimal waste rock generation. The placer method separates metals from sediments through sifting.118 In-situ method or solution mining is an in- place extraction approach by injecting a chemical solution to dis- solve the minerals in their original location and pumping back the solution including the minerals (known as the pregnant solu- tion) to the surface. There is no extraction of rocks and ore to the surface for any process.118 From the scientific point of view, the choice of mining method114 is usually determined based on four main factors: (i) the location of the mineral, (ii) the financial value of the deposit, (iii) environmental considerations, and (iv) the chemical composition of the mineral. However, other external parameters can also have a great impact, such as (i) energy efficiency, (ii) governance (char- acterizing the adequacy of national political and regulatory insti- tutions), (iii) cost (including logistic, production, and labor), (iv) social impacts (reflecting the national and regional socioeconomic factors of vulnerability such as poverty, inequalities, and demo- graphic imbalance), and (v) environmental effects (impacting waste containment including climatic and topographic factors, water resources and availability, biodiversity).119,120 The impacts of these external factors on the four mining methods are compared in a spider plot in Fig. 2b. Open surface and underground mining methods possess higher energy efficiency, lower cost, and better governance compared to placer and in-situ mining methods and are mainly used for Mn, Fe, Al, and Ni. On the other hands, placer and in-situ mining methods are considered as better social and environmentally friendly methods used for V and Co, although exhibiting lower energy efficiency and higher cost. MRS ENERGY & SUSTAINABILITY // VOLUME XX // www.mrs.org/energy-sustainability-journal 5PDF Image | cathode materials for sustainable sodium‐ion batteries
PDF Search Title:
cathode materials for sustainable sodium‐ion batteriesOriginal File Name Searched:
PerspectiveDesignOfCathodeMate.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Salgenx Redox Flow Battery Technology: Salt water flow battery technology with low cost and great energy density that can be used for power storage and thermal storage. Let us de-risk your production using our license. Our aqueous flow battery is less cost than Tesla Megapack and available faster. Redox flow battery. No membrane needed like with Vanadium, or Bromine. Salgenx flow battery
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@salgenx.com | RSS | AMP |