
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 062
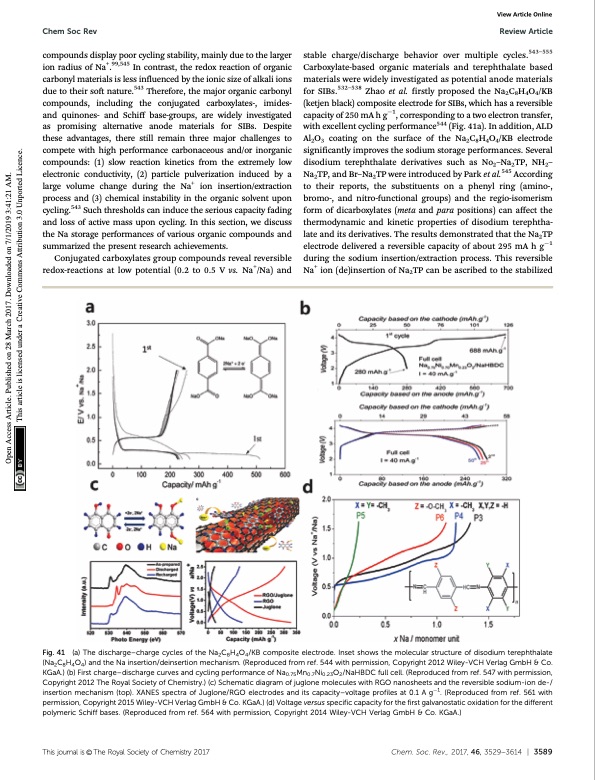
Chem Soc Rev Review Article stable charge/discharge behavior over multiple cycles.543–555 Carboxylate-based organic materials and terephthalate based materials were widely investigated as potential anode materials for SIBs.532–538 Zhao et al. firstly proposed the Na2C8H4O4/KB (ketjen black) composite electrode for SIBs, which has a reversible capacity of 250 mA h g1, corresponding to a two electron transfer, with excellent cycling performance544 (Fig. 41a). In addition, ALD Al2O3 coating on the surface of the Na2C8H4O4/KB electrode significantly improves the sodium storage performances. Several disodium terephthalate derivatives such as No2–Na2TP, NH2– Na2TP, and Br–Na2TP were introduced by Park et al.545 According to their reports, the substituents on a phenyl ring (amino-, bromo-, and nitro-functional groups) and the regio-isomerism form of dicarboxylates (meta and para positions) can affect the thermodynamic and kinetic properties of disodium terephtha- late and its derivatives. The results demonstrated that the Na2TP electrode delivered a reversible capacity of about 295 mA h g1 during the sodium insertion/extraction process. This reversible Na+ ion (de)insertion of Na2TP can be ascribed to the stabilized compounds display poor cycling stability, mainly due to the larger ion radius of Na+.99,545 In contrast, the redox reaction of organic carbonyl materials is less influenced by the ionic size of alkali ions due to their soft nature.543 Therefore, the major organic carbonyl compounds, including the conjugated carboxylates-, imides- and quinones- and Schiff base-groups, are widely investigated as promising alternative anode materials for SIBs. Despite these advantages, there still remain three major challenges to compete with high performance carbonaceous and/or inorganic compounds: (1) slow reaction kinetics from the extremely low electronic conductivity, (2) particle pulverization induced by a large volume change during the Na+ ion insertion/extraction process and (3) chemical instability in the organic solvent upon cycling.543 Such thresholds can induce the serious capacity fading and loss of active mass upon cycling. In this section, we discuss the Na storage performances of various organic compounds and summarized the present research achievements. Conjugated carboxylates group compounds reveal reversible redox-reactions at low potential (0.2 to 0.5 V vs. Na+/Na) and View Article Online Fig. 41 (a) The discharge–charge cycles of the Na2C8H4O4/KB composite electrode. Inset shows the molecular structure of disodium terephthalate (Na2C8H4O4) and the Na insertion/deinsertion mechanism. (Reproduced from ref. 544 with permission, Copyright 2012 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.) (b) First charge–discharge curves and cycling performance of Na0.75Mn0.7Ni0.23O2/NaHBDC full cell. (Reproduced from ref. 547 with permission, Copyright 2012 The Royal Society of Chemistry.) (c) Schematic diagram of juglone molecules with RGO nanosheets and the reversible sodium-ion de-/ insertion mechanism (top). XANES spectra of Juglone/RGO electrodes and its capacity–voltage profiles at 0.1 A g1. (Reproduced from ref. 561 with permission, Copyright 2015 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.) (d) Voltage versus specific capacity for the first galvanostatic oxidation for the different polymeric Schiff bases. (Reproduced from ref. 564 with permission, Copyright 2014 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.) Thisjournalis©TheRoyalSocietyofChemistry2017 Chem.Soc.Rev.,2017,46,3529--3614 | 3589 Open Access Article. Published on 28 March 2017. Downloaded on 7/1/2019 3:41:21 AM. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.PDF Image | Sodium-ion batteries present and future
PDF Search Title:
Sodium-ion batteries present and futureOriginal File Name Searched:
Sodium-ion batteries present and future.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Salgenx Redox Flow Battery Technology: Salt water flow battery technology with low cost and great energy density that can be used for power storage and thermal storage. Let us de-risk your production using our license. Our aqueous flow battery is less cost than Tesla Megapack and available faster. Redox flow battery. No membrane needed like with Vanadium, or Bromine. Salgenx flow battery
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@salgenx.com | RSS | AMP |