
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 005
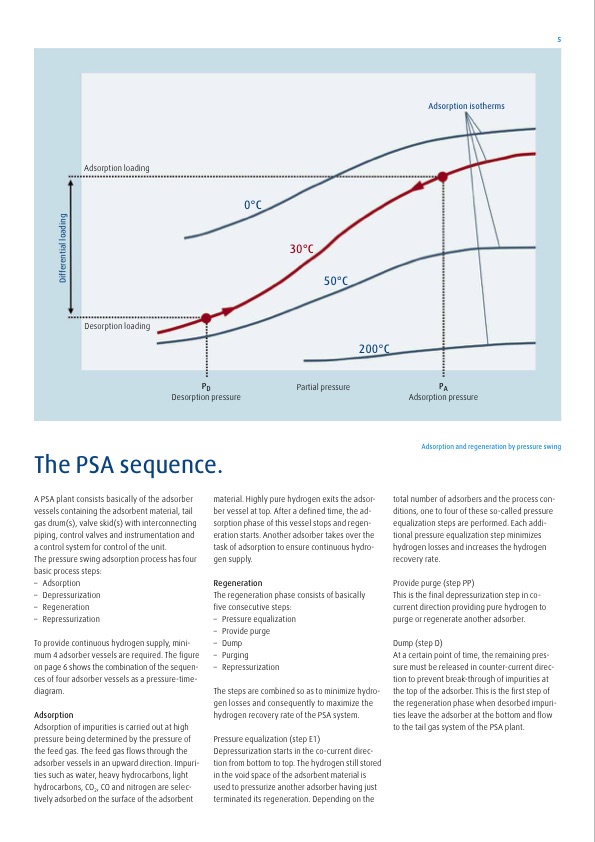
Adsorption loading Desorption loading 0°C 30°C 50°C 200°C The PSA sequence. A PSA plant consists basically of the adsorber vessels containing the adsorbent material, tail gas drum(s), valve skid(s) with interconnecting piping, control valves and instrumentation and a control system for control of the unit. The pressure swing adsorption process has four basic process steps: – Adsorption – Depressurization – Regeneration – Repressurization To provide continuous hydrogen supply, mini- mum 4 adsorber vessels are required. The figure on page 6 shows the combination of the sequen- ces of four adsorber vessels as a pressure-time- diagram. Adsorption Adsorption of impurities is carried out at high pressure being determined by the pressure of the feed gas. The feed gas flows through the adsorber vessels in an upward direction. Impuri- ties such as water, heavy hydrocarbons, light hydrocarbons, CO2, CO and nitrogen are selec- tively adsorbed on the surface of the adsorbent material. Highly pure hydrogen exits the adsor- ber vessel at top. After a defined time, the ad- sorption phase of this vessel stops and regen- eration starts. Another adsorber takes over the task of adsorption to ensure continuous hydro- gen supply. Regeneration The regeneration phase consists of basically five consecutive steps: – Pressure equalization – Provide purge – Dump – Purging – Repressurization The steps are combined so as to minimize hydro- gen losses and consequently to maximize the hydrogen recovery rate of the PSA system. Pressure equalization (step E1) Depressurization starts in the co-current direc- tion from bottom to top. The hydrogen still stored in the void space of the adsorbent material is used to pressurize another adsorber having just terminated its regeneration. Depending on the PD Desorption pressure Partial pressure PA Adsorption pressure Adsorption and regeneration by pressure swing total number of adsorbers and the process con- ditions, one to four of these so-called pressure equalization steps are performed. Each addi- tional pressure equalization step minimizes hydrogen losses and increases the hydrogen recovery rate. Provide purge (step PP) This is the final depressurization step in co- current direction providing pure hydrogen to purge or regenerate another adsorber. Dump (step D) At a certain point of time, the remaining pres- sure must be released in counter-current direc- tion to prevent break-through of impurities at the top of the adsorber. This is the first step of the regeneration phase when desorbed impuri- ties leave the adsorber at the bottom and flow to the tail gas system of the PSA plant. Adsorption isotherms 5 Differential loadingPDF Image | Hydrogen Recovery by PSA
PDF Search Title:
Hydrogen Recovery by PSAOriginal File Name Searched:
PSA-hydrogen-recovery.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |