
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 014
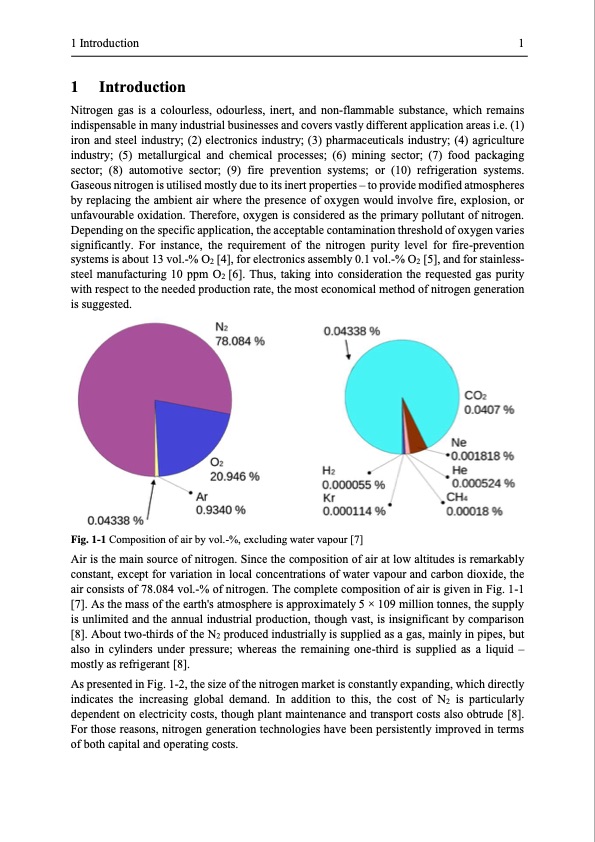
1 Introduction 1 1 Introduction Nitrogen gas is a colourless, odourless, inert, and non-flammable substance, which remains indispensable in many industrial businesses and covers vastly different application areas i.e. (1) iron and steel industry; (2) electronics industry; (3) pharmaceuticals industry; (4) agriculture industry; (5) metallurgical and chemical processes; (6) mining sector; (7) food packaging sector; (8) automotive sector; (9) fire prevention systems; or (10) refrigeration systems. Gaseous nitrogen is utilised mostly due to its inert properties – to provide modified atmospheres by replacing the ambient air where the presence of oxygen would involve fire, explosion, or unfavourable oxidation. Therefore, oxygen is considered as the primary pollutant of nitrogen. Depending on the specific application, the acceptable contamination threshold of oxygen varies significantly. For instance, the requirement of the nitrogen purity level for fire-prevention systems is about 13 vol.-% O2 [4], for electronics assembly 0.1 vol.-% O2 [5], and for stainless- steel manufacturing 10 ppm O2 [6]. Thus, taking into consideration the requested gas purity with respect to the needed production rate, the most economical method of nitrogen generation is suggested. Fig. 1-1 Composition of air by vol.-%, excluding water vapour [7] Air is the main source of nitrogen. Since the composition of air at low altitudes is remarkably constant, except for variation in local concentrations of water vapour and carbon dioxide, the air consists of 78.084 vol.-% of nitrogen. The complete composition of air is given in Fig. 1-1 [7]. As the mass of the earth's atmosphere is approximately 5 × 109 million tonnes, the supply is unlimited and the annual industrial production, though vast, is insignificant by comparison [8]. About two-thirds of the N2 produced industrially is supplied as a gas, mainly in pipes, but also in cylinders under pressure; whereas the remaining one-third is supplied as a liquid – mostly as refrigerant [8]. As presented in Fig. 1-2, the size of the nitrogen market is constantly expanding, which directly indicates the increasing global demand. In addition to this, the cost of N2 is particularly dependent on electricity costs, though plant maintenance and transport costs also obtrude [8]. For those reasons, nitrogen generation technologies have been persistently improved in terms of both capital and operating costs.PDF Image | Modelling and Simulation of Twin-Bed Pressure Swing Adsorption Plants
PDF Search Title:
Modelling and Simulation of Twin-Bed Pressure Swing Adsorption PlantsOriginal File Name Searched:
dissertation_marcinek.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |