
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 017
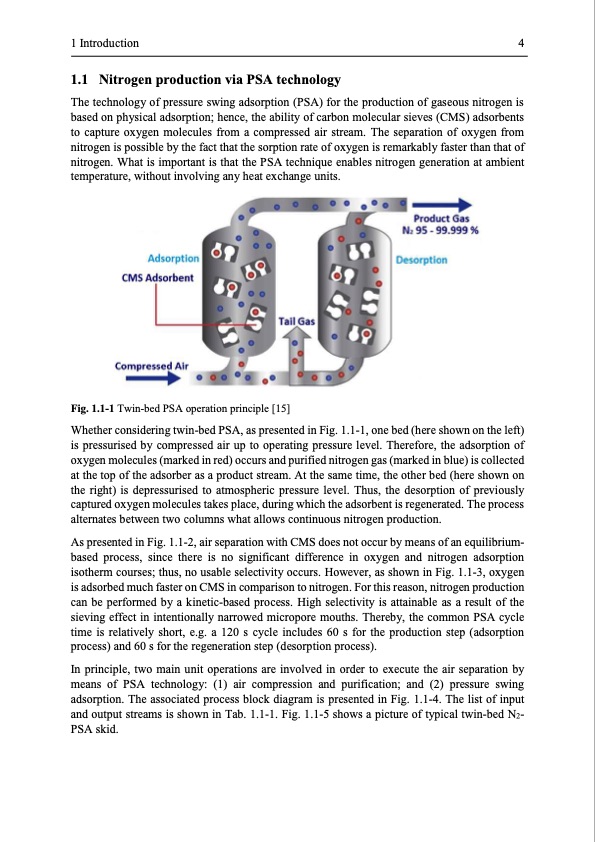
1 Introduction 4 1.1 Nitrogen production via PSA technology The technology of pressure swing adsorption (PSA) for the production of gaseous nitrogen is based on physical adsorption; hence, the ability of carbon molecular sieves (CMS) adsorbents to capture oxygen molecules from a compressed air stream. The separation of oxygen from nitrogen is possible by the fact that the sorption rate of oxygen is remarkably faster than that of nitrogen. What is important is that the PSA technique enables nitrogen generation at ambient temperature, without involving any heat exchange units. Fig. 1.1-1 Twin-bed PSA operation principle [15] Whether considering twin-bed PSA, as presented in Fig. 1.1-1, one bed (here shown on the left) is pressurised by compressed air up to operating pressure level. Therefore, the adsorption of oxygen molecules (marked in red) occurs and purified nitrogen gas (marked in blue) is collected at the top of the adsorber as a product stream. At the same time, the other bed (here shown on the right) is depressurised to atmospheric pressure level. Thus, the desorption of previously captured oxygen molecules takes place, during which the adsorbent is regenerated. The process alternates between two columns what allows continuous nitrogen production. As presented in Fig. 1.1-2, air separation with CMS does not occur by means of an equilibrium- based process, since there is no significant difference in oxygen and nitrogen adsorption isotherm courses; thus, no usable selectivity occurs. However, as shown in Fig. 1.1-3, oxygen is adsorbed much faster on CMS in comparison to nitrogen. For this reason, nitrogen production can be performed by a kinetic-based process. High selectivity is attainable as a result of the sieving effect in intentionally narrowed micropore mouths. Thereby, the common PSA cycle time is relatively short, e.g. a 120 s cycle includes 60 s for the production step (adsorption process) and 60 s for the regeneration step (desorption process). In principle, two main unit operations are involved in order to execute the air separation by means of PSA technology: (1) air compression and purification; and (2) pressure swing adsorption. The associated process block diagram is presented in Fig. 1.1-4. The list of input and output streams is shown in Tab. 1.1-1. Fig. 1.1-5 shows a picture of typical twin-bed N2- PSA skid.PDF Image | Modelling and Simulation of Twin-Bed Pressure Swing Adsorption Plants
PDF Search Title:
Modelling and Simulation of Twin-Bed Pressure Swing Adsorption PlantsOriginal File Name Searched:
dissertation_marcinek.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |