
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 086
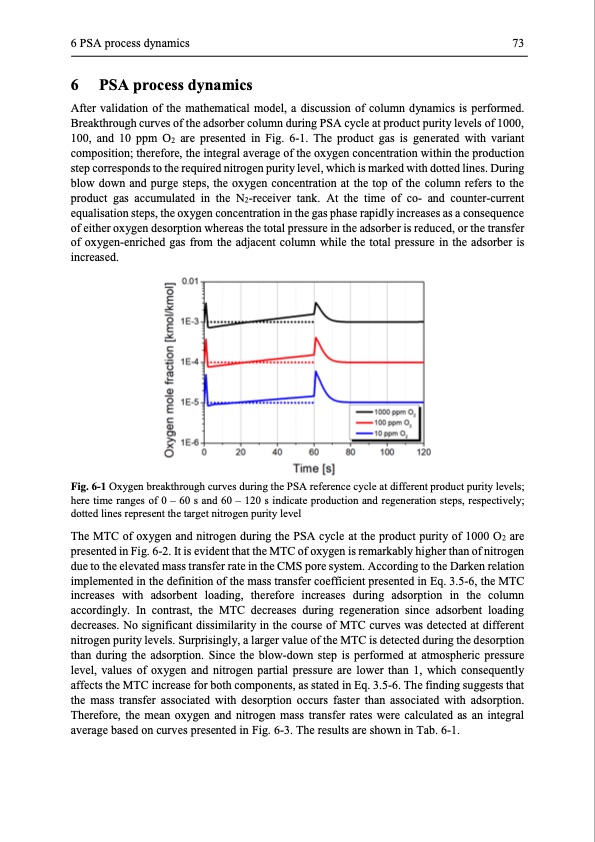
6 PSA process dynamics 73 6 PSA process dynamics After validation of the mathematical model, a discussion of column dynamics is performed. Breakthrough curves of the adsorber column during PSA cycle at product purity levels of 1000, 100, and 10 ppm O2 are presented in Fig. 6-1. The product gas is generated with variant composition; therefore, the integral average of the oxygen concentration within the production step corresponds to the required nitrogen purity level, which is marked with dotted lines. During blow down and purge steps, the oxygen concentration at the top of the column refers to the product gas accumulated in the N2-receiver tank. At the time of co- and counter-current equalisation steps, the oxygen concentration in the gas phase rapidly increases as a consequence of either oxygen desorption whereas the total pressure in the adsorber is reduced, or the transfer of oxygen-enriched gas from the adjacent column while the total pressure in the adsorber is increased. Fig. 6-1 Oxygen breakthrough curves during the PSA reference cycle at different product purity levels; here time ranges of 0 – 60 s and 60 – 120 s indicate production and regeneration steps, respectively; dotted lines represent the target nitrogen purity level The MTC of oxygen and nitrogen during the PSA cycle at the product purity of 1000 O2 are presented in Fig. 6-2. It is evident that the MTC of oxygen is remarkably higher than of nitrogen due to the elevated mass transfer rate in the CMS pore system. According to the Darken relation implemented in the definition of the mass transfer coefficient presented in Eq. 3.5-6, the MTC increases with adsorbent loading, therefore increases during adsorption in the column accordingly. In contrast, the MTC decreases during regeneration since adsorbent loading decreases. No significant dissimilarity in the course of MTC curves was detected at different nitrogen purity levels. Surprisingly, a larger value of the MTC is detected during the desorption than during the adsorption. Since the blow-down step is performed at atmospheric pressure level, values of oxygen and nitrogen partial pressure are lower than 1, which consequently affects the MTC increase for both components, as stated in Eq. 3.5-6. The finding suggests that the mass transfer associated with desorption occurs faster than associated with adsorption. Therefore, the mean oxygen and nitrogen mass transfer rates were calculated as an integral average based on curves presented in Fig. 6-3. The results are shown in Tab. 6-1.PDF Image | Modelling and Simulation of Twin-Bed Pressure Swing Adsorption Plants
PDF Search Title:
Modelling and Simulation of Twin-Bed Pressure Swing Adsorption PlantsOriginal File Name Searched:
dissertation_marcinek.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |