
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 115
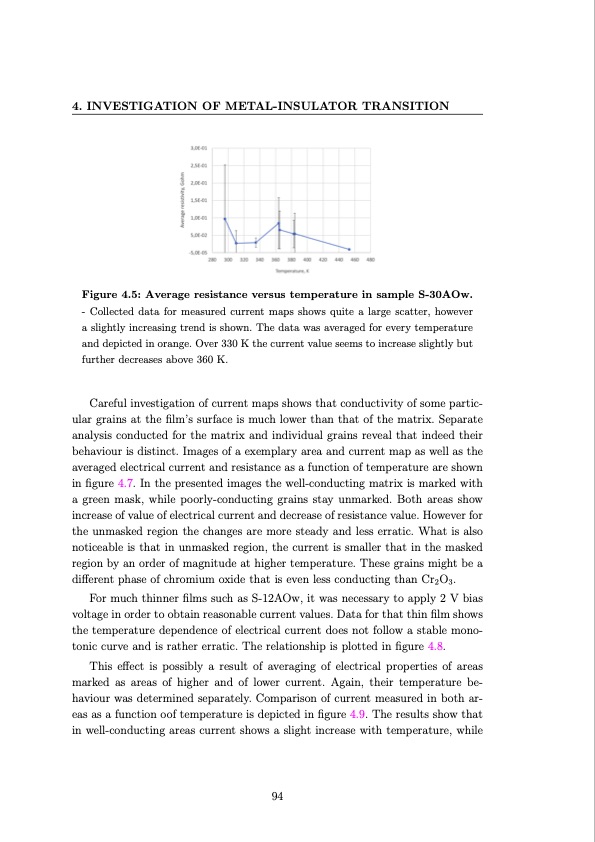
4. INVESTIGATION OF METAL-INSULATOR TRANSITION Figure 4.5: Average resistance versus temperature in sample S-30AOw. - Collected data for measured current maps shows quite a large scatter, however a slightly increasing trend is shown. The data was averaged for every temperature and depicted in orange. Over 330 K the current value seems to increase slightly but further decreases above 360 K. Careful investigation of current maps shows that conductivity of some partic- ular grains at the film’s surface is much lower than that of the matrix. Separate analysis conducted for the matrix and individual grains reveal that indeed their behaviour is distinct. Images of a exemplary area and current map as well as the averaged electrical current and resistance as a function of temperature are shown in figure 4.7. In the presented images the well-conducting matrix is marked with a green mask, while poorly-conducting grains stay unmarked. Both areas show increase of value of electrical current and decrease of resistance value. However for the unmasked region the changes are more steady and less erratic. What is also noticeable is that in unmasked region, the current is smaller that in the masked region by an order of magnitude at higher temperature. These grains might be a different phase of chromium oxide that is even less conducting than Cr2O3. For much thinner films such as S-12AOw, it was necessary to apply 2 V bias voltage in order to obtain reasonable current values. Data for that thin film shows the temperature dependence of electrical current does not follow a stable mono- tonic curve and is rather erratic. The relationship is plotted in figure 4.8. This effect is possibly a result of averaging of electrical properties of areas marked as areas of higher and of lower current. Again, their temperature be- haviour was determined separately. Comparison of current measured in both ar- eas as a function oof temperature is depicted in figure 4.9. The results show that in well-conducting areas current shows a slight increase with temperature, while 94PDF Image | Investigation of metal-insulator transition in magnetron sputtered samarium nickelate thin films
PDF Search Title:
Investigation of metal-insulator transition in magnetron sputtered samarium nickelate thin filmsOriginal File Name Searched:
Bilewska_Investigation_of_metal_insulator_transition_in_magnetron_sputtered_samarium.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2 Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2. Gamma sulfur also known as mother of pearl sulfur and nacreous sulfur... More Info
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |