
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 030
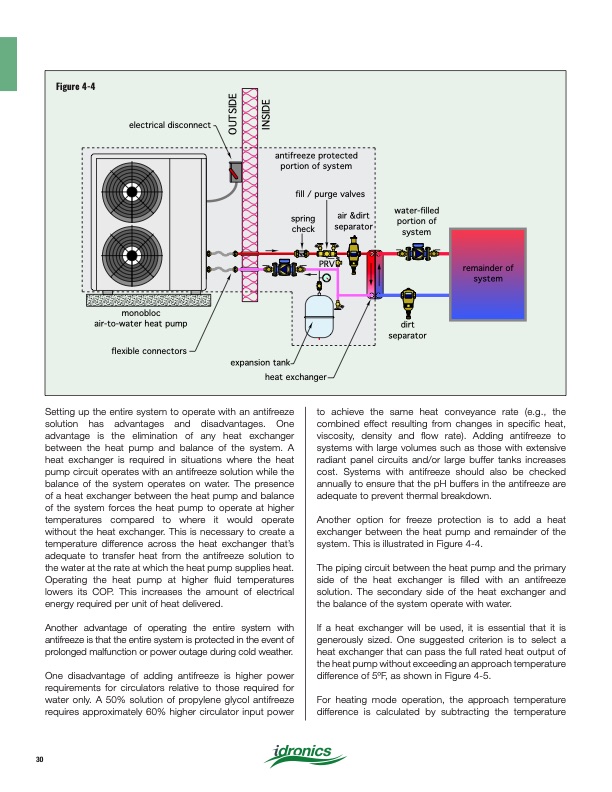
Figure 4-4 electrical disconnect antifreeze protected portion of system fill / purge valves air &dirt separator PRV expansion tank heat exchanger water-filled portion of system dirt separator spring check monobloc air-to-water heat pump flexible connectors remainder of system OUTSIDE INSIDE Setting up the entire system to operate with an antifreeze solution has advantages and disadvantages. One advantage is the elimination of any heat exchanger between the heat pump and balance of the system. A heat exchanger is required in situations where the heat pump circuit operates with an antifreeze solution while the balance of the system operates on water. The presence of a heat exchanger between the heat pump and balance of the system forces the heat pump to operate at higher temperatures compared to where it would operate without the heat exchanger. This is necessary to create a temperature difference across the heat exchanger that’s adequate to transfer heat from the antifreeze solution to the water at the rate at which the heat pump supplies heat. Operating the heat pump at higher fluid temperatures lowers its COP. This increases the amount of electrical energy required per unit of heat delivered. Another advantage of operating the entire system with antifreeze is that the entire system is protected in the event of prolonged malfunction or power outage during cold weather. One disadvantage of adding antifreeze is higher power requirements for circulators relative to those required for water only. A 50% solution of propylene glycol antifreeze requires approximately 60% higher circulator input power to achieve the same heat conveyance rate (e.g., the combined effect resulting from changes in specific heat, viscosity, density and flow rate). Adding antifreeze to systems with large volumes such as those with extensive radiant panel circuits and/or large buffer tanks increases cost. Systems with antifreeze should also be checked annually to ensure that the pH buffers in the antifreeze are adequate to prevent thermal breakdown. Another option for freeze protection is to add a heat exchanger between the heat pump and remainder of the system. This is illustrated in Figure 4-4. The piping circuit between the heat pump and the primary side of the heat exchanger is filled with an antifreeze solution. The secondary side of the heat exchanger and the balance of the system operate with water. If a heat exchanger will be used, it is essential that it is generously sized. One suggested criterion is to select a heat exchanger that can pass the full rated heat output of the heat pump without exceeding an approach temperature difference of 5oF, as shown in Figure 4-5. For heating mode operation, the approach temperature difference is calculated by subtracting the temperature 30PDF Image | Heat Pump Systems 2020
PDF Search Title:
Heat Pump Systems 2020Original File Name Searched:
idronics_27_na.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |