
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 046
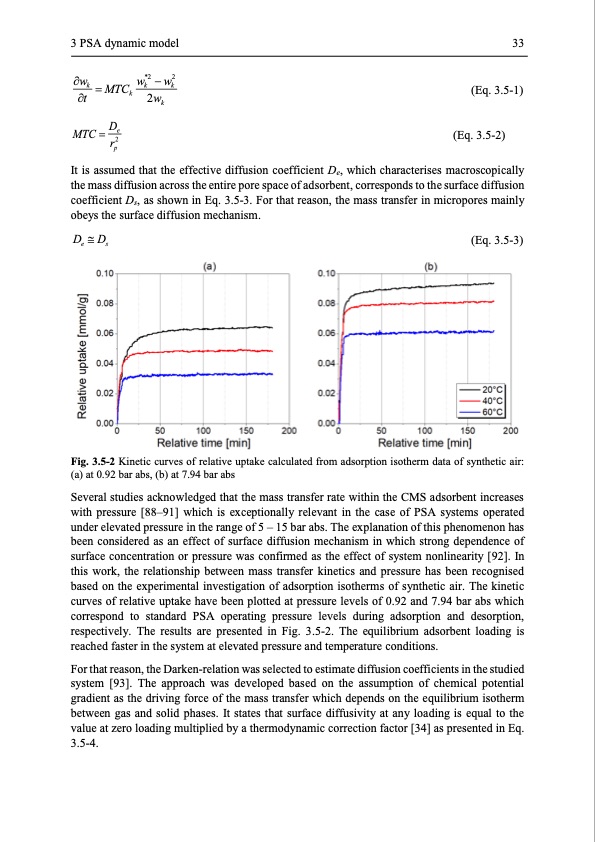
3 PSA dynamic model 33 w w*2 −w2 k=MTCk k (Eq. 3.5-1) (Eq. 3.5-2) t k 2wk MTC = De r2 p It is assumed that the effective diffusion coefficient De, which characterises macroscopically the mass diffusion across the entire pore space of adsorbent, corresponds to the surface diffusion coefficient Ds, as shown in Eq. 3.5-3. For that reason, the mass transfer in micropores mainly obeys the surface diffusion mechanism. De Ds (Eq. 3.5-3) Fig. 3.5-2 Kinetic curves of relative uptake calculated from adsorption isotherm data of synthetic air: (a) at 0.92 bar abs, (b) at 7.94 bar abs Several studies acknowledged that the mass transfer rate within the CMS adsorbent increases with pressure [88–91] which is exceptionally relevant in the case of PSA systems operated under elevated pressure in the range of 5 – 15 bar abs. The explanation of this phenomenon has been considered as an effect of surface diffusion mechanism in which strong dependence of surface concentration or pressure was confirmed as the effect of system nonlinearity [92]. In this work, the relationship between mass transfer kinetics and pressure has been recognised based on the experimental investigation of adsorption isotherms of synthetic air. The kinetic curves of relative uptake have been plotted at pressure levels of 0.92 and 7.94 bar abs which correspond to standard PSA operating pressure levels during adsorption and desorption, respectively. The results are presented in Fig. 3.5-2. The equilibrium adsorbent loading is reached faster in the system at elevated pressure and temperature conditions. For that reason, the Darken-relation was selected to estimate diffusion coefficients in the studied system [93]. The approach was developed based on the assumption of chemical potential gradient as the driving force of the mass transfer which depends on the equilibrium isotherm between gas and solid phases. It states that surface diffusivity at any loading is equal to the value at zero loading multiplied by a thermodynamic correction factor [34] as presented in Eq. 3.5-4.PDF Image | Modelling and Simulation of Twin-Bed Pressure Swing Adsorption Plants
PDF Search Title:
Modelling and Simulation of Twin-Bed Pressure Swing Adsorption PlantsOriginal File Name Searched:
dissertation_marcinek.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |