
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 047
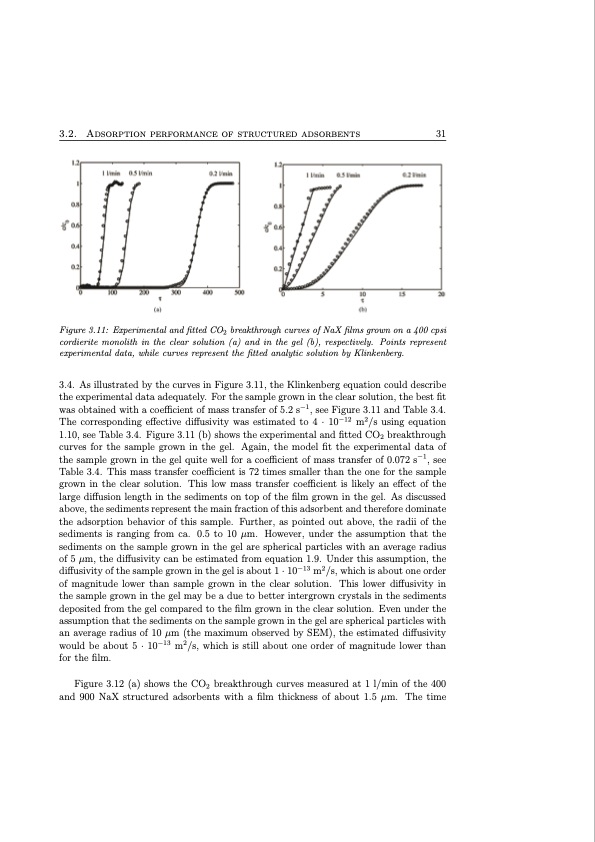
3.2. Adsorption performance of structured adsorbents 31 Figure 3.11: Experimental and fitted CO2 breakthrough curves of NaX films grown on a 400 cpsi cordierite monolith in the clear solution (a) and in the gel (b), respectively. Points represent experimental data, while curves represent the fitted analytic solution by Klinkenberg. 3.4. As illustrated by the curves in Figure 3.11, the Klinkenberg equation could describe the experimental data adequately. For the sample grown in the clear solution, the best fit was obtained with a coefficient of mass transfer of 5.2 s−1, see Figure 3.11 and Table 3.4. The corresponding effective diffusivity was estimated to 4 · 10−12 m2/s using equation 1.10, see Table 3.4. Figure 3.11 (b) shows the experimental and fitted CO2 breakthrough curves for the sample grown in the gel. Again, the model fit the experimental data of the sample grown in the gel quite well for a coefficient of mass transfer of 0.072 s−1, see Table 3.4. This mass transfer coefficient is 72 times smaller than the one for the sample grown in the clear solution. This low mass transfer coefficient is likely an effect of the large diffusion length in the sediments on top of the film grown in the gel. As discussed above, the sediments represent the main fraction of this adsorbent and therefore dominate the adsorption behavior of this sample. Further, as pointed out above, the radii of the sediments is ranging from ca. 0.5 to 10 μm. However, under the assumption that the sediments on the sample grown in the gel are spherical particles with an average radius of 5 μm, the diffusivity can be estimated from equation 1.9. Under this assumption, the diffusivity of the sample grown in the gel is about 1 · 10−13 m2/s, which is about one order of magnitude lower than sample grown in the clear solution. This lower diffusivity in the sample grown in the gel may be a due to better intergrown crystals in the sediments deposited from the gel compared to the film grown in the clear solution. Even under the assumption that the sediments on the sample grown in the gel are spherical particles with an average radius of 10 μm (the maximum observed by SEM), the estimated diffusivity would be about 5 · 10−13 m2/s, which is still about one order of magnitude lower than for the film. Figure 3.12 (a) shows the CO2 breakthrough curves measured at 1 l/min of the 400 and 900 NaX structured adsorbents with a film thickness of about 1.5 μm. The timePDF Image | Structured Zeolite Adsorbents for PSA Applications
PDF Search Title:
Structured Zeolite Adsorbents for PSA ApplicationsOriginal File Name Searched:
structured-zeolites.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |