
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 009
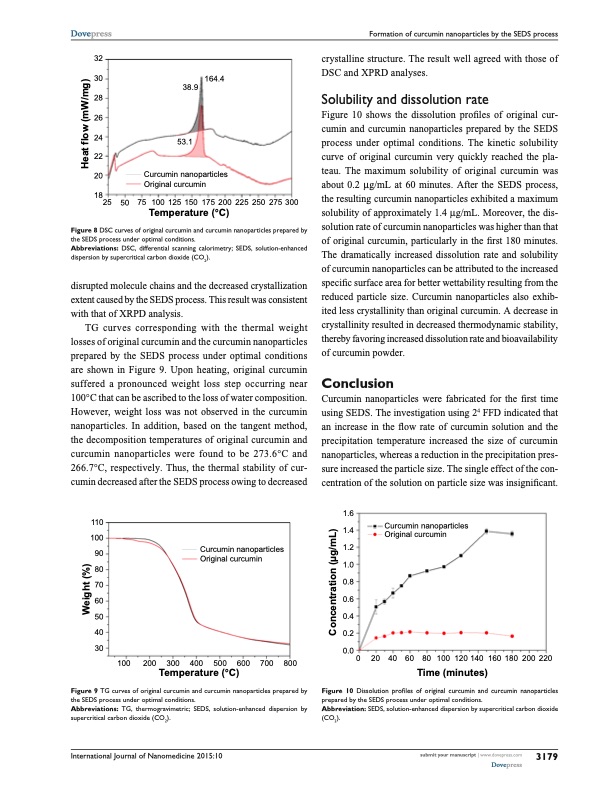
Dovepress �� �� �� �� �� �� �� ���� �� ���� ���� ����� Formation of curcumin nanoparticles by the seDs process crystalline structure. The result well agreed with those of DSC and XPRD analyses. solubility and dissolution rate Figure 10 shows the dissolution profiles of original cur- cumin and curcumin nanoparticles prepared by the SEDS process under optimal conditions. The kinetic solubility curve of original curcumin very quickly reached the pla- teau. The maximum solubility of original curcumin was about 0.2 μg/mL at 60 minutes. After the SEDS process, the resulting curcumin nanoparticles exhibited a maximum solubility of approximately 1.4 μg/mL. Moreover, the dis- solution rate of curcumin nanoparticles was higher than that of original curcumin, particularly in the first 180 minutes. The dramatically increased dissolution rate and solubility of curcumin nanoparticles can be attributed to the increased specific surface area for better wettability resulting from the reduced particle size. Curcumin nanoparticles also exhib- ited less crystallinity than original curcumin. A decrease in crystallinity resulted in decreased thermodynamic stability, thereby favoring increased dissolution rate and bioavailability of curcumin powder. Conclusion Curcumin nanoparticles were fabricated for the first time using SEDS. The investigation using 24 FFD indicated that an increase in the flow rate of curcumin solution and the precipitation temperature increased the size of curcumin nanoparticles, whereas a reduction in the precipitation pres- sure increased the particle size. The single effect of the con- centration of the solution on particle size was insignificant. �������� ������������� �������� �������� �� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ����������� �°�� Figure 8 Dsc curves of original curcumin and curcumin nanoparticles prepared by the seDs process under optimal conditions. Abbreviations: Dsc, differential scanning calorimetry; seDs, solution-enhanced dispersion by supercritical carbon dioxide (cO2). disrupted molecule chains and the decreased crystallization extent caused by the SEDS process. This result was consistent with that of XRPD analysis. TG curves corresponding with the thermal weight losses of original curcumin and the curcumin nanoparticles prepared by the SEDS process under optimal conditions are shown in Figure 9. Upon heating, original curcumin suffered a pronounced weight loss step occurring near 100°C that can be ascribed to the loss of water composition. However, weight loss was not observed in the curcumin nanoparticles. In addition, based on the tangent method, the decomposition temperatures of original curcumin and curcumin nanoparticles were found to be 273.6°C and 266.7°C, respectively. Thus, the thermal stability of cur- cumin decreased after the SEDS process owing to decreased ��� ��� �� �� �� �� �� �� �� Figure 9 Tg curves of original curcumin and curcumin nanoparticles prepared by the seDs process under optimal conditions. Abbreviations: Tg, thermogravimetric; seDs, solution-enhanced dispersion by supercritical carbon dioxide (cO2). International Journal of Nanomedicine 2015:10 ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� �������� ������������� �������� �������� �������� ������������� �������� �������� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ���� �� �� �� �� ��� ������ ��� ��� ��� ��� ���� ��������� Figure 10 Dissolution profiles of original curcumin and curcumin nanoparticles prepared by the seDs process under optimal conditions. Abbreviation: seDs, solution-enhanced dispersion by supercritical carbon dioxide (cO2). ����������� �°�� submit your manuscript | www.dovepress.com Dovepress 3179 ������ ��� ���� ���� ������� ������������� �������PDF Image | curcumin nanoparticles via dispersion by supercritical cO2
PDF Search Title:
curcumin nanoparticles via dispersion by supercritical cO2Original File Name Searched:
cucumin-nanoparticles-co2.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |