
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 049
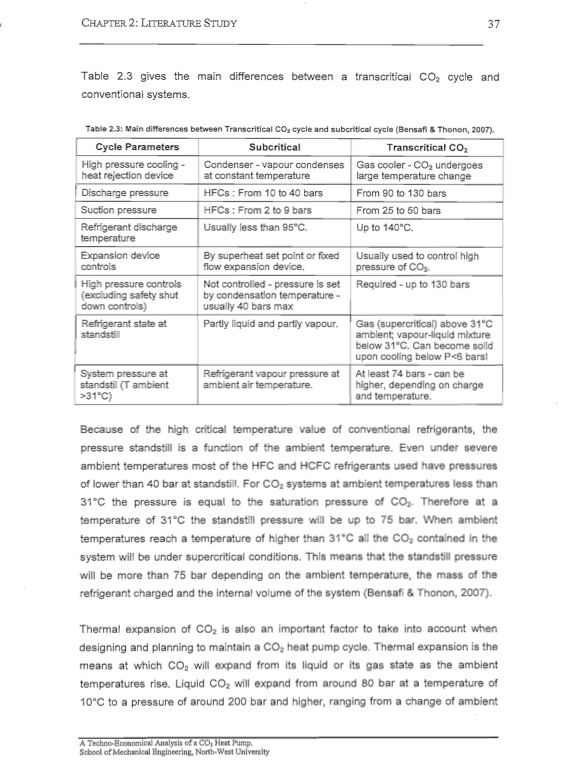
2: LITERATURE STUDY 37 Table 2.3 gives the main differences between a transcritical CO2 cycle and conventional systems. Table 2.3: Main differences between Transcritical CO2 cycle and subcritical cycle (8ensafi & Thonon, 2007). Cycle Parameters High pressure cooling - heat rejection device ~harg pressure Suction pressure Refrigerant discharge temperature Expansion device controls High pressure controls (excluding safety shut down controls) Refrigerant state at standstill SY;:'ll:::lll pressure at standstil (T ambient >31°C) Subcritical Condenser-vapour condenses at constant temperature HFCs: From 10 to 40 bars HFCs : From 2 to 9 bars Usually less than 95°C. By superheat set point or fixed flow expansion device. Not controlled - pressure is set by condensation temperature- usually 40 bars max Partly liquid and partly vapour. Refrigerant vapour pressure at ambient air temperature. • Transcritical CO2 Gas cooler- large temperature change From 90 to 130 bars From 25 to 50 bars Up to 140°C. Usually used to control high pressure of CO2 . Required - up to 130 bars Gas (supercritical) above 31°C ambient; vapour-liquid mixture below 31°C. Can become solid upon cooling below P<6 bars! At least 74 bars can be higher, depending on charge and temperature. of the high critical temperature value of conventional refrigerants, the pressure standstill is a function of the ambient temperature. Even under severe ambient temperatures most of the HFC and HCFC refrigerants used have pressures of lower than 40 bar at standstill. For CO2 systems at ambient temperatures less than 31°C the pressure is equal to the saturation pressure of CO2. Therefore at a temperature of 31°C the standstill pressure will be up to 75 bar. When ambient temperatures reach a temperature of higher than 31°C all the CO2 contained in the system will be under supercritical conditions. This means that the standstill pressure will be more than 75 bar depending on the ambient temperature, the mass of the refrigerant charged and the internal volume of the system (Bensafi & Thonon, 2007). Thermal expansion of CO2 is also an important factor to take into account when designing and planning to maintain a CO2 heat pump cycle. Thermal expansion is the means at which CO2 will expand from its liquid or its gas state as the ambient temperatures rise. Liquid CO2 will expand from around 80 bar at a temperature of D 10 C to a pressure of around 200 bar and higher, ranging from a change of ambientPDF Image | CO2 HEAT PUMP Analysis
PDF Search Title:
CO2 HEAT PUMP AnalysisOriginal File Name Searched:
co2-heat-pump-techno-analysis.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |