
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 098
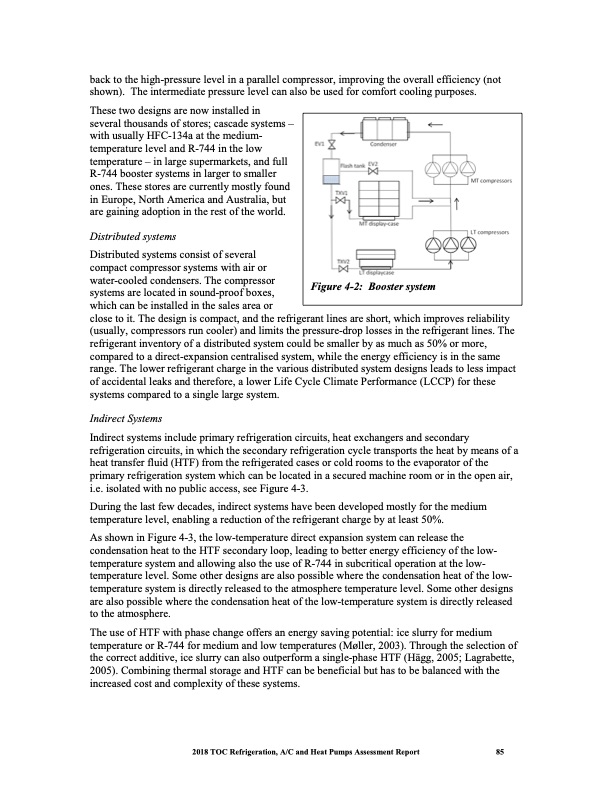
back to the high-pressure level in a parallel compressor, improving the overall efficiency (not shown). The intermediate pressure level can also be used for comfort cooling purposes. These two designs are now installed in several thousands of stores; cascade systems – with usually HFC-134a at the medium- temperature level and R-744 in the low temperature – in large supermarkets, and full R-744 booster systems in larger to smaller ones. These stores are currently mostly found in Europe, North America and Australia, but are gaining adoption in the rest of the world. Distributed systems Distributed systems consist of several compact compressor systems with air or water-cooled condensers. The compressor systems are located in sound-proof boxes, which can be installed in the sales area or close to it. The design is compact, and the refrigerant lines are short, which improves reliability (usually, compressors run cooler) and limits the pressure-drop losses in the refrigerant lines. The refrigerant inventory of a distributed system could be smaller by as much as 50% or more, compared to a direct-expansion centralised system, while the energy efficiency is in the same range. The lower refrigerant charge in the various distributed system designs leads to less impact of accidental leaks and therefore, a lower Life Cycle Climate Performance (LCCP) for these systems compared to a single large system. Indirect Systems Indirect systems include primary refrigeration circuits, heat exchangers and secondary refrigeration circuits, in which the secondary refrigeration cycle transports the heat by means of a heat transfer fluid (HTF) from the refrigerated cases or cold rooms to the evaporator of the primary refrigeration system which can be located in a secured machine room or in the open air, i.e. isolated with no public access, see Figure 4-3. During the last few decades, indirect systems have been developed mostly for the medium temperature level, enabling a reduction of the refrigerant charge by at least 50%. As shown in Figure 4-3, the low-temperature direct expansion system can release the condensation heat to the HTF secondary loop, leading to better energy efficiency of the low- temperature system and allowing also the use of R-744 in subcritical operation at the low- temperature level. Some other designs are also possible where the condensation heat of the low- temperature system is directly released to the atmosphere temperature level. Some other designs are also possible where the condensation heat of the low-temperature system is directly released to the atmosphere. The use of HTF with phase change offers an energy saving potential: ice slurry for medium temperature or R-744 for medium and low temperatures (Møller, 2003). Through the selection of the correct additive, ice slurry can also outperform a single-phase HTF (Hägg, 2005; Lagrabette, 2005). Combining thermal storage and HTF can be beneficial but has to be balanced with the increased cost and complexity of these systems. Figure 4-2: Booster system 2018 TOC Refrigeration, A/C and Heat Pumps Assessment Report 85PDF Image | Heat Pumps Technical Options
PDF Search Title:
Heat Pumps Technical OptionsOriginal File Name Searched:
RTOC-assessment-report-2018_0.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |