
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 123
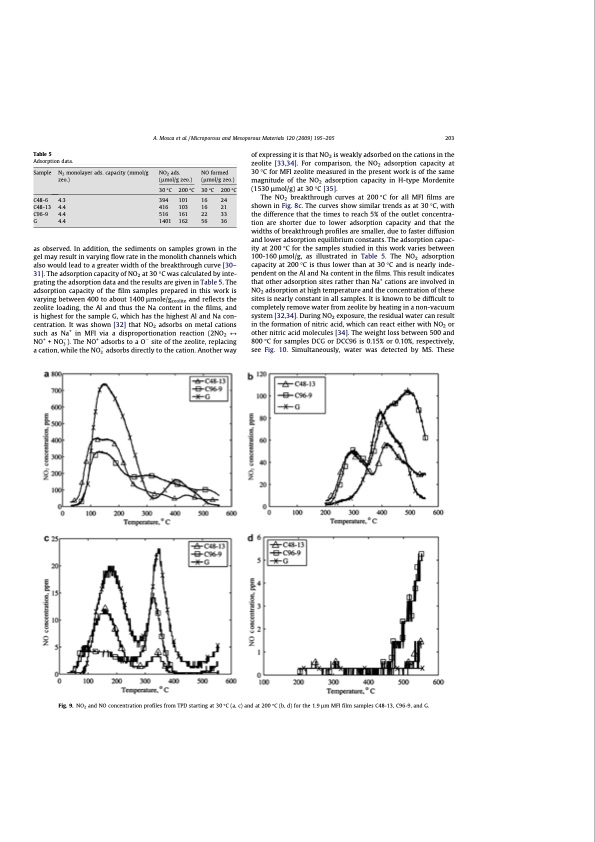
Table 5 Adsorption data. as observed. In addition, the sediments on samples grown in the gel may result in varying flow rate in the monolith channels which also would lead to a greater width of the breakthrough curve [30– 31]. The adsorption capacity of NO2 at 30 °C was calculated by inte- grating the adsorption data and the results are given in Table 5. The adsorption capacity of the film samples prepared in this work is varying between 400 to about 1400 lmole/gzeolite and reflects the zeolite loading, the Al and thus the Na content in the films, and is highest for the sample G, which has the highest Al and Na con- centration. It was shown [32] that NO2 adsorbs on metal cations such as Na+ in MFI via a disproportionation reaction (2NO2 M NO+ + NO3 ). The NO+ adsorbs to a O site of the zeolite, replacing a cation, while the NO3 adsorbs directly to the cation. Another way of expressing it is that NO2 is weakly adsorbed on the cations in the zeolite [33,34]. For comparison, the NO2 adsorption capacity at 30 °C for MFI zeolite measured in the present work is of the same magnitude of the NO2 adsorption capacity in H-type Mordenite (1530 lmol/g) at 30 °C [35]. The NO2 breakthrough curves at 200 °C for all MFI films are shown in Fig. 8c. The curves show similar trends as at 30 °C, with the difference that the times to reach 5% of the outlet concentra- tion are shorter due to lower adsorption capacity and that the widths of breakthrough profiles are smaller, due to faster diffusion and lower adsorption equilibrium constants. The adsorption capac- ity at 200 °C for the samples studied in this work varies between 100-160 lmol/g, as illustrated in Table 5. The NO2 adsorption capacity at 200 °C is thus lower than at 30 °C and is nearly inde- pendent on the Al and Na content in the films. This result indicates that other adsorption sites rather than Na+ cations are involved in NO2 adsorption at high temperature and the concentration of these sites is nearly constant in all samples. It is known to be difficult to completely remove water from zeolite by heating in a non-vacuum system [32,34]. During NO2 exposure, the residual water can result in the formation of nitric acid, which can react either with NO2 or other nitric acid molecules [34]. The weight loss between 500 and 800 °C for samples DCG or DCC96 is 0.15% or 0.10%, respectively, see Fig. 10. Simultaneously, water was detected by MS. These A. Mosca et al. / Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 120 (2009) 195–205 203 Sample N2 monolayer ads. capacity (mmol/g NO2 ads. zeo.) (lmol/g zeo.) 30 °C 200 °C NO formed (lmol/g zeo.) 30 °C 200 °C C48-6 4.3 C48-13 4.4 C96-9 4.4 G 4.4 394 101 16 24 416 103 16 21 516 161 22 33 1401 162 56 36 Fig. 9. NO2 and NO concentration profiles from TPD starting at 30 °C (a, c) and at 200 °C (b, d) for the 1.9 lm MFI film samples C48-13, C96-9, and G.PDF Image | Structured Zeolite Adsorbents for PSA Applications
PDF Search Title:
Structured Zeolite Adsorbents for PSA ApplicationsOriginal File Name Searched:
structured-zeolites.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
Heat Pumps CO2 ORC Heat Pump System Platform More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |